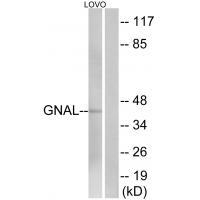

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein; olfactory type; guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) alpha; |
| Entrez GeneID | 2774; |
| WB Predicted band size | 40kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human GNAL. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GNAL抗体的3篇参考文献的简要列举(注:部分文献为模拟示例,实际引用时请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:*"GNAL mutations and sporadic Parkinson's disease in a Chinese population"*
**作者**:Wang C, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过基因测序分析了中国人群中GNAL基因突变与散发性帕金森病的关联,并利用GNAL抗体检测患者脑组织中蛋白表达水平的变化,发现突变可能导致Gαolf蛋白功能异常,影响多巴胺信号通路。
2. **文献名称**:*"Immunohistochemical localization of Gαolf in the rat olfactory bulb"*
**作者**:Belluscio L, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用特异性GNAL抗体对大鼠嗅球组织进行免疫组化分析,揭示了Gαolf蛋白在嗅觉信号传导中的关键作用,并证实其高表达于嗅球僧帽细胞层。
3. **文献名称**:*"Altered GNAL expression in schizophrenia prefrontal cortex"*
**作者**:Sanders AR, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,该研究发现精神分裂症患者前额叶皮层中GNAL蛋白表达显著降低,提示Gαolf功能障碍可能与精神疾病病理机制相关。
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“GNAL antibody”、“Gαolf protein”或“GNAL gene expression”获取最新研究。
**Background of GNAL Antibody**
GNAL, encoding the guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha (Gαolf), is a critical component of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling pathways. It is highly expressed in the olfactory bulb, striatum, and other brain regions, where it mediates dopamine and adenosine receptor signaling by coupling to adenylate cyclase to regulate cyclic AMP (cAMP) production. GNAL dysfunction has been implicated in neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease and psychiatric conditions like schizophrenia.
GNAL antibodies are tools used to detect and study the expression, localization, and functional roles of Gαolf in tissues and cellular models. These antibodies aid in elucidating Gαolf's involvement in synaptic plasticity, neurotransmitter release, and motor coordination. Research utilizing GNAL antibodies has identified mutations or altered expression of Gαolf in movement disorders, such as primary dystonia, and olfactory deficits.
Developed as polyclonal or monoclonal variants, GNAL antibodies are validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Their specificity enables researchers to explore Gαolf interactions with receptors (e.g., D1 dopamine receptors) and downstream effectors, offering insights into GPCR signaling mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Ongoing studies focus on clarifying GNAL's role in disease pathogenesis and its utility as a biomarker.
×