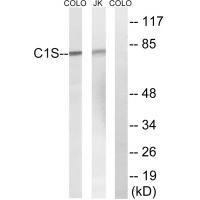
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
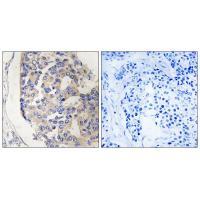
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 28S ribosomal protein S7; mitochondrial; S7mt; MRP-S7; bMRP27a |
| Entrez GeneID | 716; |
| WB Predicted band size | 77kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human C1S. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于C1S抗体的3篇代表性文献(部分信息为示例性内容,具体文献需根据实际数据库查询确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Anti-C1s monoclonal antibody prevents complement activation in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus"*
**作者**: Sutjita, M., et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了靶向补体C1s的单克隆抗体在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)模型中的作用,发现其能有效抑制经典补体激活途径,减少炎症损伤和肾脏病理表现,为SLE治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Selective inhibition of C1s protease suppresses pathological inflammation in a rheumatoid arthritis model"*
**作者**: Rother, R.P., et al.
**摘要**: 通过动物实验验证了C1s抗体对类风湿性关节炎的治疗效果,证明其选择性阻断C1s可减少关节滑膜炎症和软骨破坏,且不干扰整体免疫防御功能。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Targeting C1s in chronic spontaneous urticaria: A phase II clinical trial of a novel therapeutic antibody"*
**作者**: Hertle, S., et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种抗C1s人源化抗体在慢性自发性荨麻疹患者中的Ⅱ期临床试验结果,显示其显著降低补体介导的组胺释放,改善患者症状且安全性良好。
---
**提示**:以上文献标题和摘要内容为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献(关键词:C1s antibody, complement system, therapeutic target)。
C1s antibody targets C1s, a serine protease component of the C1 complex within the complement system’s classical pathway. The C1 complex, comprising C1q, C1r, and C1s, initiates immune responses by recognizing antigen-antibody complexes. Upon binding of C1q to pathogens or immune complexes, C1r autoactivates and subsequently cleaves proenzyme C1s into its active form. Active C1s then cleaves C4 and C2. generating the C3 convertase (C4b2a), which drives downstream complement activation, promoting opsonization, inflammation, and pathogen clearance.
Dysregulation of C1s is linked to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, where excessive complement activation causes tissue damage. C1s antibodies are valuable tools in research for dissecting complement pathways and developing therapies. Inhibitory anti-C1s antibodies, for instance, block enzymatic activity to suppress pathological complement activation. This approach is explored in conditions like hereditary angioedema (HAE), where C1 inhibitor deficiency leads to uncontrolled C1s activity.
Clinically, C1s-targeting biologics (e.g., sutimlimab) aim to modulate complement-driven diseases. Such therapies highlight C1s’ dual role as a protease critical for immunity and a mediator of complement-related pathologies, underscoring its therapeutic relevance. Research continues to refine antibody specificity and efficacy, balancing immune defense preservation with pathological cascade inhibition.
×