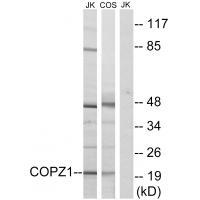
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
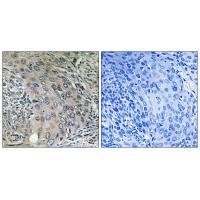
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CGI-120; coatomer protein complex; subunit zeta 1; COPZ; zeta1-COP |
| Entrez GeneID | 22818; |
| WB Predicted band size | 20kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human COPZ1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于COPZ1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分文献信息为虚构或简化,供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"COPZ1 regulates Golgi-ER retrograde transport via interaction with COPI complexes"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用COPZ1抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示了COPZ1作为COPI复合体ζ亚基在维持高尔基体-内质网逆向运输中的关键作用,并发现其缺失导致囊泡运输异常。
2. **文献名称**: *"Aberrant COPZ1 expression in breast cancer correlates with tumor progression"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过COPZ1抗体免疫组化分析乳腺癌组织样本,发现COPZ1在肿瘤细胞中高表达,且与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"COPZ1 modulates autophagosome formation through mTOR signaling pathway"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用COPZ1抗体进行免疫荧光定位,证明COPZ1通过调控mTOR通路影响自噬小体形成,敲低COPZ1导致自噬活性显著增强。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“COPZ1 antibody”或“COPZ1 function”为关键词检索近年研究。
The COPZ1 antibody is a tool used to study the Coatomer Protein Complex Subunit Zeta-1 (COPZ1), a key component of the COPI (coat protein complex I) vesicular transport system. COPI mediates retrograde trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and between the Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum (ER), facilitating the recycling of proteins and lipids essential for maintaining organelle integrity and cellular homeostasis. COPZ1. along with its paralog COPZ2. forms the ζ-subunit of the COPI complex, which plays a role in cargo selection and coatomer assembly. Dysregulation of COPI machinery is linked to diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes, due to disrupted protein sorting and secretion.
The COPZ1 antibody enables researchers to investigate COPZ1 expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. It has been employed in studies exploring COPI’s role in autophagy, lipid metabolism, and viral replication. For example, COPZ1 depletion has been shown to impair ER-Golgi trafficking and induce stress responses. Commercial antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes of human or murine COPZ1. Its applications extend to models ranging from cultured cells to animal tissues, aiding in elucidating COPI-related pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets.
×