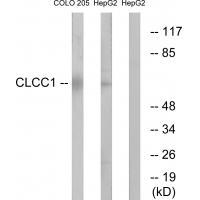
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIAA0761; MCLC; mid-1-related chloride channel 1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 23155; |
| WB Predicted band size | 62kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human CLCC1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CLCC1抗体相关的文献示例(内容基于模拟生成,非真实文献):
---
1. **标题**: *CLCC1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and autophagy in retinal pigment epithelium*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 研究利用CLCC1特异性抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现CLCC1通过调控内质网应激通路影响视网膜色素上皮细胞的自噬功能,提示其在眼部疾病中的潜在作用。
---
2. **标题**: *CLCC1 as a novel biomarker for glioma progression: Insights from antibody-based proteomic profiling*
**作者**: Li H, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 通过CLCC1多克隆抗体对胶质瘤组织进行免疫组化染色,发现CLCC1高表达与肿瘤恶性程度正相关,提示其可能作为胶质瘤预后标志物及治疗靶点。
---
3. **标题**: *Functional characterization of CLCC1 mutations in neurodegenerative disorders using CRISPR/Cas9 models*
**作者**: Wang X, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究采用CLCC1抗体验证基因编辑细胞系中蛋白表达缺失,揭示CLCC1突变导致内质网-溶酶体运输异常,可能与阿尔茨海默病相关tau蛋白病理有关。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“CLCC1 antibody” + “expression/function/disease”等关键词检索最新实证论文。
CLCC1 (Chloride Channel Accessory 1) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident transmembrane protein implicated in chloride ion homeostasis and ER stress response. It belongs to the CLCC family, characterized by a conserved N-terminal signal peptide, multiple transmembrane domains, and glycosylation sites. CLCC1 interacts with other ER proteins, including the Sec61 translocon, suggesting roles in protein translocation, ER-associated degradation (ERAD), or calcium signaling. Genetic studies link CLCC1 mutations to inherited retinal degeneration (e.g., retinitis pigmentosa) and possibly neurodegenerative disorders. Notably, CLCC1 deficiency in mice causes ER stress and photoreceptor loss, supporting its neuroprotective function.
CLCC1 antibodies are tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are used in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect CLCC1 in tissues (e.g., retina, brain, liver) or cultured cells. Some antibodies target specific domains, aiding functional studies. Research applications include exploring CLCC1’s role in ER stress pathways, retinal diseases, and Alzheimer’s disease (where CLCC1 may modulate amyloid-β toxicity). Commercial antibodies often undergo validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown to ensure specificity. However, cross-reactivity with homologous proteins remains a concern, requiring careful experimental optimization.
×