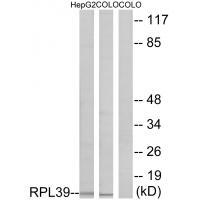

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 60S ribosomal protein L39; RPL39; |
| Entrez GeneID | 6170; |
| WB Predicted band size | 6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human RPL39. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RPL39抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*RPL39 as a Therapeutic Target in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer*
**作者**:Dave B, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用RPL39抗体检测三阴性乳腺癌组织中RPL39蛋白表达水平,发现其高表达与肿瘤干细胞特性增强及患者预后不良相关,提示RPL39可能成为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Ribosomal Protein L39 in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Novel Biomarker*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用RPL39抗体)和Western blot分析,发现RPL39在转移性结直肠癌中显著上调,并与肿瘤侵袭性和化疗耐药性相关,可能作为预后标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of RPL39 in Regulating Hepatic Cancer Cell Proliferation*
**作者**:Li H, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过siRNA敲低RPL39并结合抗体检测蛋白表达,表明RPL39通过调控mTOR信号通路促进肝癌细胞增殖,其抗体可用于评估肝癌进展的分子机制。
4. **文献名称**:*Immunohistochemical Analysis of RPL39 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer*
**作者**:Chen J, et al.
**摘要**:利用RPL39抗体对非小细胞肺癌组织进行染色,发现RPL39表达与肿瘤分期和淋巴结转移显著相关,提示其在肺癌诊断和分期中的潜在临床应用价值。
以上文献均涉及RPL39抗体在疾病机制或临床诊断中的具体应用,涵盖癌症研究的不同方向。
The RPL39 antibody is a tool used to detect ribosomal protein L39 (RPL39), a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit involved in protein synthesis. RPL39. part of the L39e protein family, is encoded by the RPL39 gene and plays a structural or catalytic role in ribosome assembly and translation. It is ubiquitously expressed across tissues, reflecting its essential function in cellular homeostasis. Researchers utilize RPL39 antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study ribosome biogenesis, protein synthesis regulation, and cellular stress responses.
Interest in RPL39 has grown due to its potential links to disease. Studies suggest its dysregulation may influence cancer progression, with elevated expression observed in certain tumors, possibly affecting cell proliferation or drug resistance. Additionally, RPL39 variants have been investigated in rare genetic disorders affecting ribosome function (ribosomopathies). The antibody's specificity is critical for distinguishing RPL39 from homologous proteins and validating its role in mechanistic or diagnostic studies. Commercial RPL39 antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes. Validation data (e.g., knockout controls) ensure reliability, as off-target binding remains a concern in ribosomal protein research. Overall, RPL39 antibodies serve as vital reagents for exploring ribosome-related biology and pathologies.
×