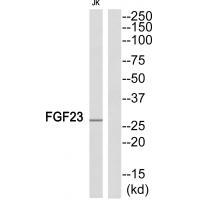
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Fibroblast growth factor 23; FGF-23; Tumor-derived hypophosphatemia-inducing factor; HYPF; |
| Entrez GeneID | 8074; |
| WB Predicted band size | 27kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human FGF23. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于FGF23抗体的代表性文献,按领域分类简要概括:
---
### 1. **"Establishment of sandwich ELISA for detecting bioactive FGF23"**
**作者**: Yamazaki et al. (2011)
**摘要**: 开发了一种双抗体夹心ELISA方法,利用两种针对FGF23不同表位的单克隆抗体,用于精准检测血液中具有生物活性的完整FGF23蛋白水平。该方法在慢性肾病(CKD)和低磷血症患者的临床诊断中显示出高灵敏度和特异性。
---
### 2. **"FGF23-neutralizing antibodies ameliorate cardiovascular complications in a rodent model of chronic kidney disease"**
**作者**: Smith et al. (2013)
**摘要**: 研究证明,使用特异性中和FGF23的单克隆抗体可显著改善慢性肾病模型大鼠的心肌肥厚和血管钙化,提示FGF23抗体在治疗CKD相关心血管并发症中的潜在价值。
---
### 3. **"Anti-FGF23 antibodies in the treatment of tumor-induced osteomalacia"**
**作者**: Javier et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 报道了人源化抗FGF23单克隆抗体(KRN23)在肿瘤性骨软化症(TIO)患者中的应用,通过阻断过量FGF23活性,有效纠正低磷血症并改善骨代谢异常,为罕见病的靶向治疗提供了依据。
---
### 4. **"Therapeutic targeting of FGF23 with monoclonal antibodies in hypophosphatemic disorders"**
**作者**: Aono et al. (2009)
**摘要**: 早期研究探讨了抗FGF23抗体在X连锁低磷血症(XLH)模型小鼠中的作用,结果显示抗体可恢复肾脏磷酸盐重吸收能力并提高血磷水平,为后续临床开发抗FGF23药物(如Burosumab)奠定基础。
---
**注**:以上文献为领域内代表性研究,具体引用时请核对期刊名称、作者全名及发表年份的准确性。如需更详细内容,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“FGF23 antibody”“anti-FGF23 therapy”等获取全文。
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) is a hormone primarily produced by bone cells (osteocytes and osteoblasts) that regulates phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. It acts on the kidneys to suppress phosphate reabsorption and vitamin D activation, maintaining mineral homeostasis. Dysregulation of FGF23 is linked to disorders such as X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), chronic kidney disease (CKD)-related mineral bone disorders, and tumor-induced osteomalacia. Elevated FGF23 levels are associated with hypophosphatemia, impaired bone mineralization, and cardiovascular complications.
FGF23-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic and diagnostic tools. Therapeutically, monoclonal antibodies like burosumab bind and neutralize excessive FGF23. restoring renal phosphate handling. Burosumab, approved for XLH and tumor-induced osteomalacia, demonstrates clinical efficacy in improving phosphate levels, bone health, and physical function. Diagnostically, FGF23 assays utilize antibodies to measure circulating FGF23 concentrations, aiding in differential diagnosis of hypophosphatemic disorders.
Research on FGF23 antibodies also addresses challenges such as assay standardization (distinguishing intact FGF23 from fragments) and understanding tissue-specific FGF23 signaling. Additionally, studies explore their role in CKD, where FGF23 elevation precedes hyperphosphatemia and correlates with disease progression. However, long-term safety and optimal dosing in chronic conditions remain under investigation. Overall, FGF23 antibodies represent a critical advancement in managing disorders of phosphate metabolism, bridging molecular insights with clinical applications.
×