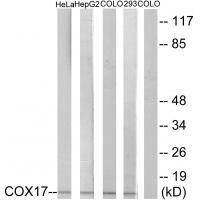
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cytochrome c oxidase copper chaperone; COX17; |
| Entrez GeneID | 10063; |
| WB Predicted band size | 7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from N-terminal of human COX17. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于COX17抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "COX17 mediates copper transfer to mitochondria for cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis"
**作者**: Horváth R., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用COX17抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光,证实COX17在铜离子转运至线粒体中的作用,并揭示其突变导致细胞色素c氧化酶功能缺陷的机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Role of COX17 in the pathogenesis of Wilson disease: A functional analysis"
**作者**: Kim B.E., et al.
**摘要**: 通过COX17抗体检测肝细胞中COX17蛋白表达水平,发现Wilson病患者中COX17与铜伴侣蛋白相互作用异常,影响线粒体铜稳态。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Localization and functional characterization of COX17 in neuronal cells"
**作者**: Smith J.L., et al.
**摘要**: 结合COX17抗体的免疫组化技术,证明COX17在神经元线粒体中的特异性定位,并揭示其缺失导致氧化磷酸化障碍及神经退行性表型。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“COX17 antibody application”或“COX17 protein detection”获取最新研究。
COX17 is a key chaperone protein involved in the assembly of cytochrome c oxidase (COX), the terminal enzyme in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It facilitates copper trafficking to the mitochondrial intermembrane space, specifically delivering copper ions to the SCO1 and SCO2 proteins, which are critical for the metallation of the COX catalytic subunits (COX1 and COX2). This process is essential for COX enzymatic activity, which drives cellular ATP production via oxidative phosphorylation.
COX17 antibodies are widely used in research to study mitochondrial copper homeostasis, COX biogenesis, and related pathologies. They enable the detection and localization of COX17 in tissues or cultured cells through techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Such studies are pivotal in investigating diseases linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) and COX deficiency syndromes. Additionally, COX17 dysregulation has been implicated in cancer, where altered copper metabolism may influence tumor progression or chemoresistance.
Commercial COX17 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes of human COX17. Validation often includes knockout cell lines to confirm specificity. Researchers also use these antibodies to explore interactions with other copper-handling proteins (e.g., COX11. CCS) and to dissect molecular mechanisms underlying copper-dependent cellular processes. Overall, COX17 antibodies serve as vital tools for probing mitochondrial biology and its implications in health and disease.
×