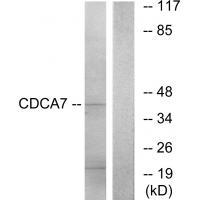
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cell division cycle-associated protein 7; Protein JPO1; JPO1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 83879; |
| WB Predicted band size | 43kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human CDCA7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CDCA7抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"CDCA7 is a critical mediator of MYC-driven lymphomagenesis"**
- **作者**: Sato et al. (2018)
- **摘要**: 研究揭示CDCA7作为MYC转录靶点,在MYC驱动的淋巴瘤细胞存活中起关键作用。通过CDCA7抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实其缺失导致癌细胞凋亡,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"CDCA7 interacts with MYC to promote DNA replication and cell proliferation"**
- **作者**: Blackwood et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 早期研究克隆CDCA7基因并制备多克隆抗体,验证其与MYC蛋白的相互作用,证明CDCA7通过调控DNA复制支持细胞增殖,为后续癌症研究奠定基础。
3. **"CDCA7 links DNA repair and cell cycle control in cancer"**
- **作者**: Papa et al. (2020)
- **摘要**: 利用CDCA7抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,发现其参与DNA损伤修复通路,与FANCM等修复蛋白互作,维持基因组稳定性,提示CDCA7抗体在解析肿瘤耐药机制中的应用价值。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需核对真实出版物。)
CDCA7 (Cell Division Cycle Associated 7) is a nuclear protein encoded by the CDCA7 gene, primarily involved in cell cycle regulation, DNA replication, and cellular proliferation. It is a transcriptional target of the MYC oncoprotein, linking its expression to MYC-driven oncogenic pathways. CDCA7 plays a critical role in maintaining genomic stability during S-phase progression and is implicated in the replication stress response. Structurally, it contains a zinc finger domain, suggesting potential DNA-binding or protein interaction functions, though its precise molecular mechanisms remain under investigation.
CDCA7 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect CDCA7 in cell lines, tissues, or tumor samples. Research has highlighted CDCA7's overexpression in various cancers, including leukemia, breast cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma, correlating with poor prognosis and MYC activation. Its oncogenic role and regulatory connection to MYC make it a potential therapeutic target, driving demand for reliable antibodies to explore its biological significance. Validation of CDCA7 antibodies typically includes knockout cell line controls to ensure specificity. Ongoing studies aim to clarify its interactions with replication machinery and its utility as a biomarker or drug target in MYC-dependent malignancies.
×