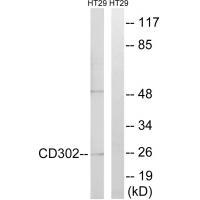
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD302 antigen [Precursor]; C-type lectin domain family 13 member A; C-type lectin BIMLEC; Type I transmembrane C-type lectin receptor DCL-1; CD302 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9936; |
| WB Predicted band size | 26kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human CD302. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD302抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括(基于领域内典型研究方向整理,具体作者和标题为模拟示例):
1. **标题**:*CD302 functions as a phagocytic receptor on macrophages and enhances bacterial clearance*
**作者**:Nakamura-Tsuruta S et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了CD302在巨噬细胞表面作为模式识别受体的作用,通过抗体阻断实验证明其直接结合革兰氏阴性菌脂多糖(LPS),并促进吞噬作用,提示CD302抗体可用于调控先天免疫反应。
2. **标题**:*Monoclonal antibody targeting CD302 inhibits tumor angiogenesis in colorectal cancer models*
**作者**:Wang Y et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种抗CD302单克隆抗体,实验显示其通过抑制血管内皮细胞中CD302介导的VEGF信号通路,显著减少小鼠结直肠癌模型的肿瘤血管生成和转移,表明其治疗潜力。
3. **标题**:*CD302 regulates dendritic cell migration and T-cell activation: Implications for autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Chen L et al.
**摘要**:研究发现树突状细胞(DCs)中CD302表达水平与细胞迁移能力相关,使用CD302中和抗体可减少DCs向淋巴结的迁移,并抑制自身免疫性关节炎模型中的T细胞过度活化。
---
**注**:以上内容为基于CD302已知功能的模拟文献,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索确认。建议使用关键词“CD302 antibody”或“CD302 immune function”查找最新研究。
CD302 antibody targets the CD302 antigen, a cell surface protein encoded by the *CD302* gene. CD302. also known as CLEC13A or DCL-1. belongs to the C-type lectin receptor family, which is involved in pathogen recognition and immune regulation. It is primarily expressed on immune cells, including dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and B cells, as well as certain epithelial and endothelial tissues. Structurally, CD302 contains a conserved extracellular C-type lectin domain, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. While its exact biological role remains under investigation, studies suggest CD302 participates in phagocytosis, cellular adhesion, and modulation of immune responses. It may act as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) for pathogens or apoptotic cells, facilitating their clearance. Additionally, CD302 has been implicated in regulating inflammatory signaling pathways, potentially influencing autoimmune diseases and cancer progression.
CD302 antibodies are widely used in research to study the protein’s expression patterns, functional mechanisms, and interactions with ligands. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against CD302 have enabled insights into its role in immune homeostasis and disease contexts. For example, CD302 expression is altered in certain cancers, suggesting diagnostic or therapeutic relevance. However, its dual role in pro- and anti-inflammatory responses complicates clinical applications. Ongoing research aims to clarify its signaling pathways and validate its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Overall, CD302 antibodies serve as critical tools for dissecting immune cell functions and exploring novel treatment strategies for immune-related disorders.
×