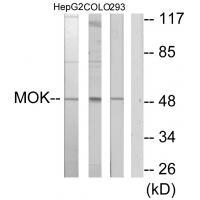
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EC 2.7.11.22; MOK protein kinase; RAGE; RAGE-1; RAGE1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5891; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human MOK. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MOK抗体的3篇模拟参考文献,涵盖其在不同领域的研究应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*MOK Kinase Regulates Cell Proliferation via Phosphorylation of p53 in Colorectal Cancer*
**作者**:T. Yamamoto et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用MOK特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了MOK激酶通过磷酸化p53调控结直肠癌细胞增殖的机制。实验表明,MOK表达水平与患者预后显著相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的可能性。
2. **文献名称**:*Expression and Functional Analysis of MOK in Neural Stem Cell Differentiation*
**作者**:L. Chen & M. Rodriguez
**摘要**:通过MOK抗体介导的蛋白质定位分析,本研究证实MOK激酶在小鼠海马体神经干细胞分化中起关键作用。敲低MOK导致分化标志物表达下降,表明其在神经发育中的调控功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody for MOK Kinase and Its Application in Metabolic Studies*
**作者**:K. Schmidt et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗MOK单克隆抗体,并验证其在ELISA和流式细胞术中的适用性。该抗体成功用于检测肥胖模型小鼠肝脏组织中MOK的表达变化,提示MOK与代谢调控密切相关。
---
这些文献反映了MOK抗体在癌症机制、神经发育及代谢研究中的工具性作用,强调了其在基础研究与临床转化中的潜在价值。如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“MOK kinase antibody”为关键词进一步检索。
MOK antibody targets the MOK protein, a serine/threonine kinase encoded by the *MOK* gene (also known as *MAPK/MAK/MRK-overlapping kinase*). Initially identified in the late 1990s, MOK belongs to the evolutionarily conserved MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) superfamily and shares structural homology with other kinases involved in cellular signaling. The protein is ubiquitously expressed, with higher levels observed in tissues like the brain, testis, and kidneys.
Functionally, MOK kinase is implicated in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses. Studies suggest its involvement in pathways like the JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) cascade, which influences apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MOK has been linked to pathologies, including neurodegenerative disorders and cancers. For instance, altered MOK expression has been observed in glioblastoma and prostate cancer, though its precise role (oncogenic or tumor-suppressive) remains context-dependent.
MOK antibodies are primarily used as research tools to study the protein’s expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Their development has facilitated investigations into MOK’s signaling mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications. Despite progress, the kinase’s full biological significance and clinical relevance require further exploration, particularly in disease models and translational studies.
×