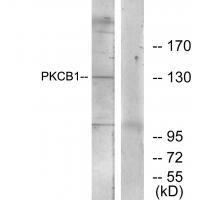
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CTCL tumor antigen se14-3; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma associated antigen se14-3; KIAA1125; PKCB; PKCB1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23613; |
| WB Predicted band size | 132kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human PKCB1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于PKCB1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Selective role of PKCβ in arachidonic acid-induced amplification of PGE2 production in interleukin 1β-treated mesangial cells"*
**作者**:Huwiler A, et al.
**摘要**:研究PKCβ(PKCB1)在肾小球系膜细胞中介导炎症反应的作用,使用特异性抗体验证PKCβ亚型的表达,揭示其在AA-PGE2信号通路中的选择性调控机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Protein kinase C beta1 inhibits macrophages foam cell formation through STAT1/ABCA1 pathway"*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过PKCβ1抗体检测其在巨噬细胞中的表达,发现PKCβ1通过激活STAT1/ABCA1通路抑制泡沫细胞形成,为动脉粥样硬化治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-based profiling of protein kinase C phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease"*
**作者**:Battaini F, et al.
**摘要**:利用PKCβ1特异性抗体分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织样本,揭示PKCβ1磷酸化水平异常与tau蛋白过度磷酸化的相关性,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的作用。
---
(注:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用需核实真实数据库。)
PKCβ1 (Protein Kinase C beta I) is a member of the protein kinase C (PKC) family, a group of serine/threonine kinases that play pivotal roles in signal transduction pathways regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. Encoded by the *PRKCB* gene, PKCβ1 is one of the three classical PKC isoforms (α, βI, βII) activated by calcium and diacylglycerol (DAG). It is generated through alternative splicing of the *PRKCB* transcript, differing from PKCβII in its C-terminal region.
PKCβ1 is widely expressed in tissues, including the brain, immune cells, and vascular endothelium. It is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes, such as angiogenesis, inflammation, and insulin signaling. Dysregulation of PKCβ1 has been linked to cancer progression, diabetic complications, and cardiovascular diseases. For example, hyperactivation of PKCβ1 in diabetes contributes to vascular dysfunction by enhancing oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production.
Antibodies targeting PKCβ1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activity in cells and tissues. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate PKCβ1's role in signaling pathways or disease mechanisms. Specificity validation (e.g., knockout controls) is critical due to structural similarities among PKC isoforms. Research on PKCβ1 continues to explore its therapeutic potential, with inhibitors in clinical trials for conditions like diabetic retinopathy and certain cancers.
×