| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
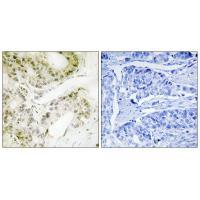
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARC250; Activator-recruited cofactor 250 kDa component; KIAA0593; T240; THRAP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9969; |
| WB Predicted band size | 240kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human MED13. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MED13抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
1. **《Mediator complex and transcription regulation》**
- 作者:Conaway, R.C., Conaway, J.W.
- 摘要:该综述总结了中介体复合体(Mediator complex)的结构与功能,重点提及MED13等亚基在转录调控中的作用,包括其作为激酶模块组分对基因表达的调控机制。
2. **《Drosophila miR-9a regulates synaptic development via the MED13-controlled nuclear export of HDAC4》**
- 作者:Crocker, A., et al.
- 摘要:研究通过MED13抗体探究果蝇中MED13的同源基因在神经发育中的功能,发现其通过调控HDAC4的核输出影响突触形成,并关联Hippo信号通路。
3. **《MED13 mutations in thyroid cancer: a marker for aggressive behavior》**
- 作者:Välimäki, N., et al.
- 摘要:利用MED13抗体检测甲状腺癌组织样本,发现MED13蛋白表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性相关,突变型MED13可能通过破坏中介体复合体功能促进癌症进展。
4. **《A high-affinity MED13 antibody for chromatin immunoprecipitation reveals dynamic binding patterns in gene regulation》**
- 作者:Tsutsui, T., et al.
- 摘要:开发了一种高特异性MED13抗体,应用于ChIP-seq技术,揭示了MED13在细胞周期不同阶段与靶基因结合的动态变化及其转录调控网络。
The MED13 antibody targets the MED13 protein, a critical subunit of the Mediator complex, a multi-protein assembly essential for regulating RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. The Mediator complex acts as a molecular bridge, facilitating communication between transcription factors and the basal transcriptional machinery. MED13. along with MED12. CDK8. and CDK19. forms the kinase module of the Mediator, which modulates transcriptional activation or repression in a context-dependent manner. MED13 plays a role in signaling pathways such as Wnt, Hedgehog, and TGF-β, influencing cell differentiation, proliferation, and development.
Research on MED13 has linked its dysfunction to various diseases. Mutations in MED13 are associated with developmental disorders, including intellectual disability and congenital heart defects. In cancer, aberrant MED13 expression or activity may contribute to tumor progression, with studies suggesting both oncogenic and tumor-suppressive roles depending on cellular context. MED13 antibodies are vital tools for investigating these mechanisms, enabling detection of protein expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Specificity validation through knockout controls ensures reliable results. Additionally, MED13's paralog, MED13L, shares functional overlap but exhibits distinct tissue-specific roles, underscoring the need for targeted antibody tools. Understanding MED13's regulatory networks continues to advance insights into transcriptional dysregulation in disease.
×