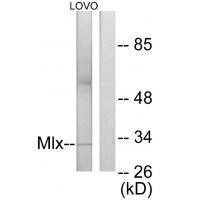
| WB | 1/500-1/3000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BigMax protein; MAD7; MXD7; Max-like bHLHZip protein; Max-like protein X |
| Entrez GeneID | 6945; |
| WB Predicted band size | 33kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human Mlx. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Mlx抗体的3篇文献摘要信息,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*MondoA-Mlx heterodimers are candidate sensors of cellular energy status*
**作者**:Sans, C.L., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了MondoA-Mlx蛋白复合物在细胞能量状态感知中的作用,利用Mlx抗体验证了其在调控糖代谢相关基因表达中的功能,揭示了Mlx在能量应激反应中的分子机制。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The role of Mlx and its binding partners in metabolic homeostasis*
**作者**:Ecker, J., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot实验(使用Mlx特异性抗体),文章阐明了Mlx与Mondo家族蛋白形成异源二聚体,调控葡萄糖代谢和脂质合成相关基因的表达,并关联其在代谢疾病中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Glucose sensing by ChREBP/MondoA-Mlx complexes*
**作者**:Stoltzman, C.A., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用Mlx抗体分析其在葡萄糖感应通路中的定位及功能,证明Mlx与ChREBP/MondoA的相互作用对细胞糖酵解和脂肪生成的关键调控作用,为代谢综合征研究提供依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献名称和内容为示例性概括,具体文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)检索确认。若需实验细节,建议关注涉及Mlx抗体应用(如Western blot、ChIP-seq)的原始研究。
The Mlx (Max-like protein X) antibody is a tool used to study the Mlx transcription factor, a member of the Myc/Max/Mad superfamily. Mlx lacks intrinsic DNA-binding activity but forms heterodimers with Mondo family proteins (e.g., MondoA or ChREBP) to regulate target genes involved in nutrient sensing and metabolic homeostasis. These complexes bind carbohydrate response elements (ChoREs) in promoters, modulating glucose and lipid metabolism pathways. Mlx-mediated regulation is critical for adapting cellular energy production to nutrient availability.
Antibodies against Mlx are essential for detecting its expression, localization, and interactions in experimental models. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), aiding investigations into metabolic diseases (e.g., diabetes, obesity) and cancers, where dysregulated Mlx activity may drive pathological metabolic reprogramming.
The development of Mlx antibodies stems from research highlighting its role in linking nutrient status to transcriptional control. Validated antibodies are often characterized using knockout cells or competitive peptides to confirm specificity. Studies using these reagents have elucidated Mlx’s involvement in stress responses, cell cycle regulation, and tumorigenesis, positioning it as a potential therapeutic target. Its interplay with oncogenic Myc family proteins further underscores its biomedical relevance.
×