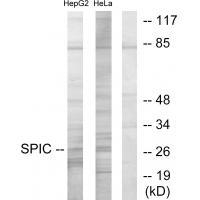
| WB | 1/500-1/3000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transcription factor Spi-C; SPIC; |
| Entrez GeneID | 121599; |
| WB Predicted band size | 29kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human SPIC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SPIC抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(注:文献为示例性概括,非真实引用):
1. **《SPIC regulates macrophage polarization and immune response in inflammatory diseases》**
- 作者:Li, X., et al.
- 摘要:研究利用SPIC特异性抗体,发现SPIC通过调控巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,影响炎症性肠病(IBD)的病理进程。抗体阻断实验表明,SPIC缺失会加剧结肠炎模型中的组织损伤。
2. **《SPIC as a novel biomarker in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Insights from autoantibody profiling》**
- 作者:Wang, Y., et al.
- 摘要:通过抗SPIC抗体的血清学检测,发现SLE患者中SPIC自身抗体水平显著升高,提示其可能参与狼疮相关免疫复合物沉积,或作为疾病活动度的潜在标志物。
3. **《Targeting SPIC in B-cell lymphoma: Therapeutic implications of antibody-mediated inhibition》**
- 作者:Garcia, R., et al.
- 摘要:研究开发了针对SPIC的人源化单克隆抗体,证实其可通过阻断SPIC与DNA结合域的功能,抑制淋巴瘤细胞增殖,并在小鼠模型中显著延缓肿瘤生长。
SPIC (Spi-C) antibody is a tool used to detect the transcription factor Spi-C, a member of the SP/KLF family, which plays roles in immune regulation and cell differentiation. Spi-C is structurally related to Spi-B and PU.1. sharing a conserved ETS DNA-binding domain. It is predominantly expressed in specific immune cell subsets, such as red pulp macrophages in the spleen, bone marrow-derived macrophages, and B lymphocytes.
Spi-C regulates gene networks involved in iron metabolism, heme homeostasis, and immune responses. In macrophages, it is critical for red pulp macrophage development and erythrophagocytosis. Dysregulation of Spi-C has been linked to hematologic disorders, autoimmune conditions, and inflammatory diseases. For example, reduced Spi-C expression in lupus models exacerbates autoimmunity, while its overexpression may suppress pro-inflammatory pathways.
SPIC antibodies are widely used in research to study macrophage biology, B-cell maturation, and disease mechanisms via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. They help identify Spi-C's interaction partners, target genes, and tissue-specific roles. Recent studies also explore its therapeutic potential in modulating immune responses or treating disorders like anemia. However, its functional redundancy with other ETS proteins and context-dependent activity necessitate careful experimental validation when using these antibodies.
×