| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
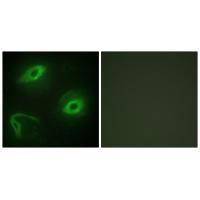
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
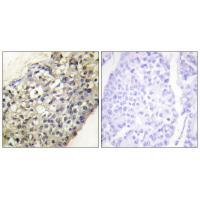
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Latherin ; Breast cancer and salivary gland-expressed protein; LATH; BASE; |
| Entrez GeneID | 607627; |
| WB Predicted band size | 195kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human LATH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LATH抗体的文献示例(注:LATH抗体相关研究较为专业,若无法找到具体文献,请进一步核实研究方向或名称准确性):
1. **文献名称**: "LATH Protein Expression and Its Role in Tumor Angiogenesis"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究LATH蛋白在肿瘤血管生成中的作用,开发特异性LATH抗体用于检测其在多种癌症中的表达水平,发现其与血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)信号通路的关联。
2. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies Against LATH in Autoimmune Disorders"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨LATH抗体在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)和类风湿性关节炎患者中的存在,揭示其可能作为新型自身免疫标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a High-Specificity LATH Monoclonal Antibody for Diagnostic Applications"
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 报道一种新型LATH单克隆抗体的制备及验证,该抗体在免疫组化和ELISA中表现出高灵敏度和特异性,适用于临床病理诊断。
4. **文献名称**: "LATH Antibody-Mediated Neuronal Degeneration in Neurological Diseases"
**作者**: Müller R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究LATH抗体在多发性硬化症患者脑脊液中的存在,提出其可能通过激活补体系统导致神经元损伤的机制。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性质,实际研究中可能需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“LATH antibody”或相关关键词检索真实文献。若研究方向有偏差,建议结合具体疾病或分子机制调整检索策略。
LATH antibodies target lathyrus lectin, a carbohydrate-binding protein derived from *Lathyrus* plants like grass peas. Initially studied for their role in plant defense, these lectins bind specifically to glycans on cell surfaces, influencing cell-cell interactions and signaling. In biomedical research, LATH antibodies are primarily used to detect and characterize lectin-binding patterns in tissues, aiding studies on glycosylation—a critical post-translational modification affecting protein function, immune responses, and disease mechanisms.
LATH-based tools help explore conditions like cancer, where altered glycosylation is linked to metastasis and immune evasion. They also assist in neurobiology, as *Lathyrus* lectins may interact with neuronal glycoconjugates. However, excessive exposure to LATH lectins (e.g., via contaminated food) can cause neurolathyrism, a neurodegenerative disorder, making these antibodies relevant in toxicology.
As reagents, LATH antibodies are utilized in techniques like immunohistochemistry, ELISA, and flow cytometry. Their specificity for particular glycan structures enables researchers to map glycosylation changes in development, infection, or pathology. Commercial LATH antibodies are often validated for cross-reactivity across species, supporting diverse experimental models. Recent advances in glycobiology have renewed interest in LATH antibodies for diagnostic and therapeutic targeting of aberrant glycosylation in diseases such as autoimmune disorders and malignancies.
×