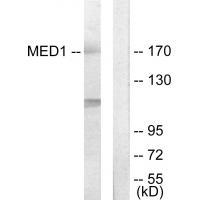
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
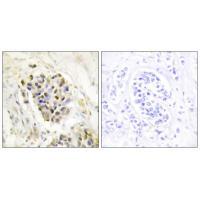
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mediator complex subunit 1; |
| Entrez GeneID | 5469; |
| WB Predicted band size | 170kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human MED1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
1. **"MED1 phosphorylation promotes its association with mediator to regulate gene transcription"**
- 作者:Malik, S. et al.
- 摘要:研究MED1通过磷酸化修饰增强其与中介体复合物的结合,调控靶基因(如脂代谢相关基因)的转录活性,实验中利用MED1抗体进行ChIP-seq分析其染色质结合位点。
2. **"MED1 is a mediator of the estrogen receptor-driven oncogenic pathway in breast cancer"**
- 作者:Jiang, H. et al.
- 摘要:揭示MED1作为雌激素受体(ER)的共激活因子,通过抗体染色和敲除实验证明其在乳腺癌中促进肿瘤生长及耐药性,临床样本中MED1高表达与预后不良相关。
3. **"Antibody-specific validation for mediator subunit MED1 in transcriptional regulation assays"**
- 作者:Taatjes, D.J. et al.
- 摘要:系统验证多种商业化MED1抗体的特异性,比较其在Western blot、免疫荧光及ChIP中的表现,为研究中介体复合物功能提供方法学参考。
4. **"MED1 coordinates PPARγ-dependent adipocyte differentiation by stabilizing the mediator complex"**
- 作者:Ge, K. et al.
- 摘要:阐明MED1通过结合PPARγ调控脂肪细胞分化,使用MED1抗体阻断实验证实其在维持中介体复合物稳定性及脂类代谢基因激活中的关键作用。
The MED1 antibody targets the Mediator Complex Subunit 1 (MED1), a critical component of the Mediator complex, a multi-protein assembly that regulates RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. MED1. also known as TRAP220 or DRIP205. serves as a bridge between transcription factors and the core Mediator complex, facilitating gene-specific transcriptional activation. It plays a pivotal role in nuclear receptor-mediated signaling pathways, including those involving estrogen, thyroid hormone, and PPARγ, making it essential for metabolic regulation, cell differentiation, and oncogenesis.
MED1 antibodies are widely used in research to study transcriptional mechanisms, protein-protein interactions, and chromatin remodeling. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, ChIP-seq, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to detect MED1 expression, localization, and binding partners. Dysregulation of MED1 is linked to cancers (e.g., breast, prostate), metabolic disorders, and developmental defects, driving interest in its functional characterization.
Commercial MED1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with specificity validated via knockout controls. Researchers must verify cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat) and account for MED1’s splice variants. Its role in enhancer-promoter looping and super-enhancer formation underscores its importance in gene network regulation, positioning MED1 antibodies as vital tools in epigenetics and disease biology studies.
×