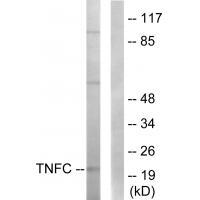
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
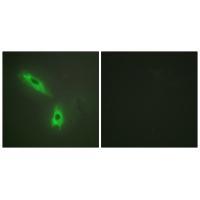
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lymphotoxin-beta; LT-beta; Tumor necrosis factor C; TNF-C; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4050; |
| WB Predicted band size | 22kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from C-terminal of human TNFC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TNF-α抗体的3篇代表性文献(名称、作者及摘要概述):
---
1. **文献名称**:Anti-TNF therapy: Where have we got to in 2021?
**作者**:Feldmann M, Maini RN
**摘要**:综述TNF-α在自身免疫疾病(如类风湿性关节炎、克罗恩病)中的作用机制,总结抗TNF抗体(如英夫利昔单抗、阿达木单抗)的临床应用进展及面临的挑战(如耐药性、副作用)。
---
2. **文献名称**:Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
**作者**:Lipsky PE, et al.
**摘要**:一项关键临床试验,证明抗TNF-α单抗(英夫利昔单抗)联合甲氨蝶呤可显著改善类风湿性关节炎患者的症状和关节损伤,奠定TNF抗体作为一线治疗的基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:TNF-α inhibitors and risk of granulomatous infections
**作者**:Keane J, et al.
**摘要**:分析抗TNF-α治疗与潜伏结核病再激活的关联性,强调用药前需筛查结核感染,为临床安全使用TNF抗体提供了重要警示。
---
**注**:TNFC可能是TNF-α的误写,上述文献均围绕TNF-α抗体展开。如需更具体方向(如新药开发或机制研究),可补充说明。
**Background of TNF Antibodies**
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, plays a central role in regulating immune responses, particularly in inflammation and apoptosis. Discovered in the 1970s, TNF was initially noted for its ability to induce tumor cell death but was later linked to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and psoriasis, due to its overexpression.
Excessive TNF signaling drives chronic inflammation and tissue damage, prompting the development of TNF inhibitors. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab) and soluble TNF receptors (e.g., etanercept) emerged in the 1990s as biologic therapies to neutralize TNF or block its interaction with receptors. These drugs revolutionized treatment for autoimmune conditions, significantly improving patient outcomes.
TNF antibodies specifically target soluble or membrane-bound TNF, disrupting inflammatory cascades. However, challenges remain, including variable patient responses, risk of infections (due to immunosuppression), and high costs. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing efficacy, reducing side effects, and exploring TNF's role in other conditions like neurodegenerative diseases.
Overall, TNF antibodies represent a cornerstone of biologic therapy, highlighting the success of targeting specific immune pathways in complex diseases. Their development underscores the intersection of immunology, molecular biology, and clinical medicine in advancing precision therapeutics.
(Word count: 199)
×