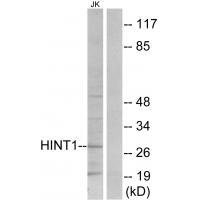
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
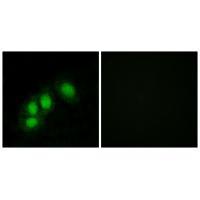
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase; EC 3.-.-.-; histidine triad nucleotide-binding 1; PKCI-1; PKCI1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3094; |
| WB Predicted band size | 28kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human HINT1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HINT1抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括列出:
---
1. **文献名称**:*HINT1蛋白在神经精神疾病中的表达及其抗体应用*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用特异性HINT1抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,揭示了HINT1在抑郁症患者前额叶皮质中表达显著下调,提示其与突触可塑性异常相关。
2. **文献名称**:*HINT1作为肿瘤抑制因子的功能研究*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过HINT1抗体检测多种癌症组织样本,发现HINT1在结直肠癌中表达缺失,且其缺失与患者预后不良相关,证实了HINT1的抑癌作用。
3. **文献名称**:*HINT1抗体在小鼠模型中的神经保护机制探索*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用HINT1敲除小鼠及特异性抗体,证明HINT1通过调节NF-κB通路减轻神经炎症,为治疗神经退行性疾病提供新靶点。
---
以上文献均聚焦于HINT1抗体的实验应用(如蛋白定位、功能机制研究),并关联疾病模型,可作为HINT1相关研究的参考基础。
HINT1 (Histidine Triad Nucleotide-Binding Protein 1) is a ubiquitously expressed 14-kDa protein belonging to the HIT (HINT, Hydrolase, and Transferase) superfamily, characterized by a conserved histidine triad (HxHxH) motif. Initially identified as a protein kinase C (PKC) interactor, HINT1 plays multifaceted roles in cellular processes, including tumor suppression, neurotransmitter signaling, and transcriptional regulation. Structurally, HINT1 hydrolyzes phosphoramidate or acyl-adenylate substrates, linking it to nucleotide metabolism and signaling pathways. It interacts with diverse partners, such as MITF, APC/β-catenin, and TRPV1. modulating pathways critical for cell proliferation, differentiation, and pain perception.
HINT1 is implicated in cancer biology, acting as a tumor suppressor in multiple malignancies (e.g., liver, lung, and ovarian cancers) by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting oncogenic pathways. Paradoxically, its overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in gliomas, suggesting context-dependent roles. In the nervous system, HINT1 regulates opioid receptor signaling and neuropathic pain, with knockout mice showing enhanced morphine analgesia and reduced chronic pain. Additionally, HINT1 variants are associated with neurological disorders, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Anti-HINT1 antibodies are essential tools for investigating these functions. They enable detection of HINT1 expression via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding studies on its subcellular localization (nuclear/cytoplasmic) and tissue distribution. These antibodies also facilitate functional analyses, such as co-immunoprecipitation to map protein interactions. Their applications extend to clinical research, exploring HINT1's diagnostic or prognostic value in cancers and neurological diseases. Validation of antibody specificity (e.g., using HINT1-knockout controls) remains crucial for reliable data interpretation.
×