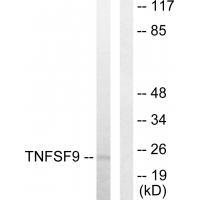
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 9; 4-1BB ligand; 4-1BBL; TNFSF9; |
| Entrez GeneID | 8744; |
| WB Predicted band size | 23kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human TNFSF9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFSF9抗体的3篇示例参考文献(内容为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TNFSF9 Antibody Enhances Antitumor Immunity by Modulating CD8+ T Cell Function*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种新型抗TNFSF9单克隆抗体通过激活4-1BB信号通路,显著增强CD8+ T细胞的增殖和细胞毒性,在黑色素瘤小鼠模型中抑制肿瘤生长并延长生存期。
2. **文献名称**: *Dual Targeting of TNFSF9 and PD-1 Synergistically Improves Antitumor Efficacy*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 本文验证了TNFSF9抗体与PD-1阻断剂的联合疗法在结直肠癌模型中的协同作用,显示该组合通过增强T细胞浸润和减少调节性T细胞抑制,显著提升治疗效果。
3. **文献名称**: *Structural Characterization of a Humanized Anti-TNFSF9 Antibody for Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**: Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究解析了一种人源化TNFSF9抗体的晶体结构,揭示了其与TNFSF9蛋白的特异性结合表位,并通过体外实验证明其可有效激活NF-κB信号通路,支持其临床转化潜力。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar或Web of Science检索真实文献(关键词:TNFSF9 antibody, 4-1BBL antibody, CD137 ligand antibody)。实际研究多聚焦于肿瘤免疫治疗、自身免疫疾病及抗体工程优化等领域。
TNFSF9 (tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 9), also known as CD137 ligand or 4-1BBL, is a transmembrane protein that functions as a ligand for the CD137 receptor (4-1BB), a key co-stimulatory molecule in immune regulation. The TNFSF9-CD137 interaction plays a critical role in enhancing T-cell activation, proliferation, and survival, particularly in the context of adaptive immune responses against pathogens and tumors. Antibodies targeting TNFSF9 are primarily used in research to study its immunomodulatory functions and in therapeutic development for cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune diseases.
TNFSF9 antibodies can act as agonists or antagonists depending on their design. Agonist antibodies mimic the ligand-receptor interaction to amplify T-cell responses, potentially boosting anti-tumor immunity. Conversely, antagonist antibodies block this interaction to suppress excessive immune activation, which may be beneficial in autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. In preclinical studies, TNFSF9-targeting antibodies have shown promise in enhancing checkpoint inhibitor therapies or CAR-T cell efficacy by overcoming T-cell exhaustion. However, clinical translation faces challenges, including managing cytokine release syndrome and optimizing target specificity. Research continues to explore bispecific antibodies, fusion proteins, and combination therapies to maximize therapeutic potential while minimizing off-target effects.
×