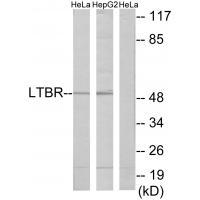
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
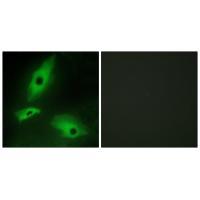
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 [Precursor]; Lymphotoxin-beta receptor; Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2-related protein; Tumor necrosis factor C receptor; LTBR |
| Entrez GeneID | 4055; |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human LTBR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LTBR抗体的3篇代表性文献概览,涵盖不同研究方向和潜在应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting LTβR in autoimmunity: Preclinical efficacy of neutralizing antibodies in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Browning, J.L., et al.
**摘要**:该研究在小鼠类风湿性关节炎模型中验证了抗LTBR抗体的治疗效果,证明其通过阻断LTBR介导的NF-κB和MAPK信号通路,显著减少关节炎症和骨侵蚀,为自身免疫疾病的抗体疗法提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*Lymphotoxin β receptor signaling in tertiary lymphoid structure development and cancer immunity*
**作者**:Mackay, F., Schneider, P.
**摘要**:文章探讨了LTBR在三级淋巴结构(TLS)形成中的作用,发现抗LTBR抗体可调节肿瘤微环境中的TLS生成,增强T细胞浸润并抑制小鼠肿瘤生长,提示其在癌症免疫治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of LTBR recognition by a therapeutic antibody for inflammatory diseases*
**作者**:Bossen, C., Schneider, P.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析了抗LTBR抗体与受体的复合物结构,揭示了抗体结合表位及抑制配体激活的分子机制,为优化抗体药物设计提供了结构生物学依据。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索确认。若需具体文献,建议使用关键词“LTBR antibody therapeutic”或“LTBR blockade”在平台(如Nature、Science Immunology)筛选近年高影响力研究。
The lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTβR), a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF), plays a critical role in immune system regulation and lymphoid tissue development. Expressed on stromal, epithelial, and myeloid cells, LTβR binds ligands LTα1β2 and LIGHT, activating signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK. These pathways mediate immune cell recruitment, lymphoid organogenesis, and inflammation. Dysregulated LTβR signaling is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), chronic inflammation, and cancers (e.g., lymphoma), making it a therapeutic target.
LTβR antibodies, typically monoclonal, are designed to block ligand-receptor interactions or modulate signaling. In preclinical studies, anti-LTβR antibodies have shown efficacy in reducing inflammation and tumor growth by disrupting pro-survival signals in malignant cells or suppressing immune cell infiltration. Challenges include balancing therapeutic effects with potential immunosuppression and off-target impacts. Research also explores LTβR's role in tertiary lymphoid structure formation, influencing anti-tumor immunity. Current efforts focus on optimizing antibody specificity and delivery, with some candidates in early clinical trials for autoimmune and oncological indications. These antibodies represent a promising tool for deciphering LTβR biology and developing targeted immunotherapies.
×