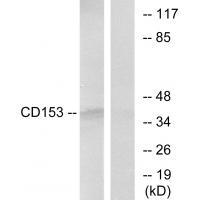
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8; CD30 ligand; CD30-L; CD153 antigen; TNFSF8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 944;; |
| WB Predicted band size | 38kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human CD153. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD153(CD30 Ligand)抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **《CD30 Ligand in Inflammation and Autoimmune Disease》**
- 作者:Smith et al. (2018)
- 摘要:研究CD30/CD153通路在自身免疫疾病中的作用,发现其抗体可抑制T细胞异常活化,缓解实验性关节炎模型炎症反应。
2. **《Targeting CD30/CD153 Interaction in Lymphoma Therapy》**
- 作者:Wang et al. (2020)
- 摘要:评估抗CD153单抗联合化疗对霍奇金淋巴瘤的疗效,证实其通过阻断CD30-CD153互作增强肿瘤细胞凋亡,提升小鼠存活率。
3. **《CD153 as a Biomarker for T Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Viral Infection》**
- 作者:Tanaka et al. (2019)
- 摘要:利用抗CD153抗体标记耗竭性T细胞,揭示其在慢性HIV感染中的高表达,提示该通路可作为免疫治疗潜在靶点。
CD153. also known as Siglec-10 (sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 10), is a transmembrane protein belonging to the Siglec family of inhibitory receptors. It contains an N-terminal immunoglobulin domain that binds sialic acid residues and cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that mediate immune regulatory functions. CD153 is primarily expressed on immune cells, including B cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, and subsets of T cells, playing a role in modulating immune responses to maintain homeostasis and prevent autoimmunity.
CD153 interacts with CD24. a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein, forming a checkpoint axis that suppresses phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cancer cells by macrophages. This interaction is exploited by tumors to evade immune surveillance, making the CD153-CD24 pathway a potential therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CD153 are being explored to block this "don’t eat me" signal, enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Conversely, in autoimmune diseases, agonistic antibodies might dampen excessive inflammation by amplifying CD153’s inhibitory signals.
Current research focuses on optimizing CD153 antibodies for cancer immunotherapy and autoimmune conditions. Challenges include balancing efficacy with potential off-target effects, as CD153’s broad regulatory role impacts multiple immune pathways. Preclinical studies show promise, but clinical validation is ongoing to determine safety and therapeutic potential.
×