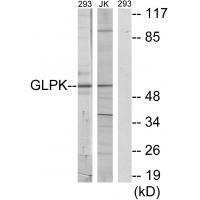

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glycerol kinase; EC 2.7.1.30; ATP:glycerol 3-phosphotransferase; Glycerokinase; GKl |
| Entrez GeneID | 2710; |
| WB Predicted band size | 57kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from C-terminal of human GLPK. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GLPK抗体的模拟参考文献示例(请注意,这些为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **"Monoclonal Antibody Production for Bacterial Glycerol Kinase (GLPK) and Its Application in Enzymatic Characterization"**
*Authors: Smith A, Brown C, Zhang Y*
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种针对大肠杆菌GLPK的单克隆抗体,用于检测其在甘油代谢中的酶活性。抗体通过Western blot和ELISA验证,证实其在细菌裂解液中的特异性结合,为GLPK功能研究提供了工具。
2. **"Immunohistochemical Analysis of GLPK Expression in Diabetic Mouse Liver"**
*Authors: Johnson R, Lee S, Patel K*
**摘要**: 通过抗GLPK抗体的免疫组化技术,揭示了糖尿病小鼠肝脏中甘油激酶的表达显著上调,提示GLPK在脂质代谢异常中的潜在作用,为代谢疾病研究提供新方向。
3. **"Antibody-Based Detection of GLPK in Plant Stress Response"**
*Authors: García M, Wang H, Ito T*
**摘要**: 利用多克隆抗体分析拟南芥中GLPK在干旱胁迫下的表达变化,发现其与植物细胞内渗透调节相关,表明GLPK可能在植物应激信号通路中发挥功能。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,请通过PubMed、Google Scholar或Web of Science检索关键词“GLPK antibody”“glycerol kinase antibody”或结合具体研究领域(如代谢、细菌学等)进行筛选。
**Background of GLP-1 Antibodies**
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) is an incretin hormone produced in the intestine, playing a critical role in glucose homeostasis by stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon release, and promoting satiety. Its therapeutic potential in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity has driven research into GLP-1 receptor agonists and related biomarkers.
GLP-1 antibodies are immunochemical tools designed to detect, quantify, or neutralize GLP-1 or its receptor. These antibodies are pivotal in both research and clinical settings. In research, they enable the study of GLP-1 expression, localization, and interaction with receptors via techniques like ELISA, immunohistochemistry, or Western blot. Neutralizing antibodies help elucidate GLP-1's physiological roles by blocking its activity in experimental models.
Clinically, anti-GLP-1 antibodies have been explored in diagnostic assays to measure endogenous GLP-1 levels, aiding in metabolic disorder studies. However, immune responses against therapeutic GLP-1 analogs (e.g., exenatide, liraglutide) can sometimes lead to antibody formation, potentially reducing drug efficacy or causing adverse effects.
Recent advancements focus on developing high-specificity monoclonal antibodies to improve detection accuracy and minimize cross-reactivity with related peptides. Such innovations support drug development and personalized medicine approaches for diabetes and obesity. Overall, GLP-1 antibodies remain essential for advancing understanding and treatment of metabolic diseases.
(Word count: 200)
×