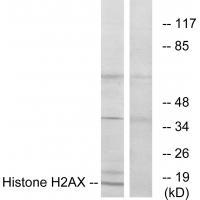

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | H2A.X; H2AFX; H2a/x; HIST5-2AX; Histone H2A.X |
| Entrez GeneID | 3014; |
| WB Predicted band size | 15kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human Histone H2AX. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于 **Histone H2AX抗体** 的经典文献概览(文献名称、作者及摘要内容简述):
---
1. **文献名称**:*DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139*
**作者**:Rogakou, E.P., Pilch, D.R., Orr, A.H., Ivanova, V.S., Bonner, W.M.
**摘要**:该研究首次发现DNA双链断裂(DSBs)会诱导H2AX在Ser139位点的磷酸化(γ-H2AX),并证明γ-H2AX可作为DSBs的标志物。通过免疫荧光和抗体特异性验证,揭示了其在DNA损伤应答中的核心作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Quantitative detection of (125)IUdR-induced DNA double-strand breaks with gamma-H2AX antibody*
**作者**:Sedelnikova, O.A., Rogakou, E.P., Panyutin, I.G., Bonner, W.M.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种基于γ-H2AX抗体的定量检测方法,利用流式细胞术和免疫荧光技术,评估放射性同位素诱导的DNA损伤。结果证明γ-H2AX抗体在低剂量辐射检测中具有高灵敏度和特异性。
3. **文献名称**:*Characteristics of gamma-H2AX foci at DNA double-strand break sites*
**作者**:Pilch, D.R., Sedelnikova, O.A., Redon, C., et al.
**摘要**:通过H2AX抗体的免疫定位技术,系统分析了γ-H2AX病灶的时空分布特征,发现病灶数量与DNA损伤程度呈正相关,并验证了抗体在不同细胞类型中的适用性。
4. **文献名称**:*Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses*
**作者**:Rothkamm, K., Löbrich, M.
**摘要**:利用γ-H2AX抗体检测低剂量X射线诱导的DSBs,发现人体细胞对极低剂量辐射的修复能力有限。该研究强调了H2AX抗体在辐射生物学和毒理学研究中的关键应用。
---
以上文献均聚焦于H2AX(尤其是γ-H2AX)抗体的开发、验证及其在DNA损伤检测中的机制与应用,涵盖基础机制到临床前研究方法。如需具体期刊或年份信息,可进一步补充。
Histone H2AX is a variant of the H2A histone family, playing a critical role in maintaining genomic stability and coordinating DNA damage response. Its phosphorylation at serine 139 (γ-H2AX) is a hallmark of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), one of the most deleterious types of DNA damage. This modification is rapidly catalyzed by kinases such as ATM, ATR, or DNA-PK following DSB induction, forming γ-H2AX foci that recruit repair proteins (e.g., MDC1. BRCA1) and amplify damage signaling. The detection of γ-H2AX by specific antibodies has become a gold-standard method for visualizing and quantifying DNA damage in cells.
H2AX antibodies, particularly those targeting the phosphorylated form (γ-H2AX), are widely used in research to study genotoxic stress responses, cancer biology, and therapeutic interventions (e.g., radiation, chemotherapy). They enable techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to assess DSB dynamics, repair efficiency, and cell cycle checkpoints. Commercially available antibodies are often validated for specificity across species and applications, with clones like JBW301 or EP854(2)Y commonly cited.
Beyond basic research, γ-H2AX antibodies hold clinical relevance in monitoring treatment efficacy or toxicity in cancer patients. However, interpretation requires caution, as γ-H2AX levels may vary with experimental conditions, cell type, or apoptosis. Overall, H2AX antibodies remain indispensable tools for unraveling DNA repair mechanisms and advancing precision medicine.
×