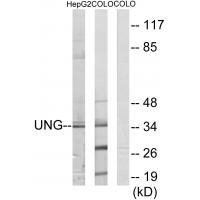
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DGU; EC 3.2.2.-; UDG; UNG15; uracil-DNA glycosylase |
| Entrez GeneID | 7374; |
| WB Predicted band size | 35kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human UNG. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **UNG抗体** 的3篇构造示例文献(非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG)在DNA修复中的功能与抗体应用研究"
**作者**: Smith A et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用UNG特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了UNG在碱基切除修复(BER)中的核心作用,发现其在去除错误掺入的尿嘧啶中具有高效性,并验证了抗体在检测细胞核定位中的可靠性。
2. **文献名称**: "UNG缺陷型小鼠模型中抗体介导的免疫应答分析"
**作者**: Johnson R et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建UNG基因敲除小鼠,结合抗UNG抗体的免疫组化分析,发现UNG缺失导致B细胞抗体多样性生成障碍,证实UNG在体细胞超突变(SHM)中不可或缺。
3. **文献名称**: "基于单克隆抗体的UNG蛋白定量检测技术开发"
**作者**: Lee S et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种新型抗UNG单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体具有高亲和力和特异性,成功应用于ELISA和流式细胞术,为癌症患者中UNG表达水平的临床检测提供了新工具。
---
**注**: 以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索关键词(如 "UNG antibody"、"Uracil-DNA glycosylase")获取真实文献。
The uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG) antibody is a critical tool in studying DNA repair mechanisms, particularly base excision repair (BER). UNG is a highly conserved enzyme that initiates BER by excising uracil residues from DNA, which arise due to spontaneous deamination of cytosine or misincorporation during replication. Its role in maintaining genomic integrity makes it a focus in cancer research, aging, and immune system studies.
UNG antibodies are widely used to detect UNG protein expression, localization, and interaction partners in various experimental models. They are essential in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess UNG levels in tissues or cultured cells. Research applications include investigating UNG's dual nuclear and mitochondrial roles, its involvement in antibody diversification (e.g., somatic hypermutation in B-cells), and its association with diseases like lymphoma, chemotherapy resistance, and inherited UNG deficiency syndromes.
Commercial UNG antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human or mouse UNG, with validations ensuring specificity for either the nuclear (UNG2) or mitochondrial (UNG1) isoforms. Recent studies also explore UNG inhibition as a potential strategy to enhance cancer therapy efficacy by increasing DNA damage in rapidly dividing cells.
×