
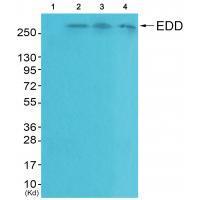
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
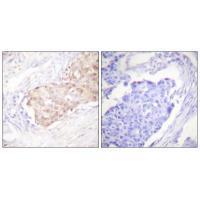
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAK; CD167a antigen; Cell adhesion kinase; Discoidin receptor tyrosine kinase; EC 2.7.1.112 |
| Entrez GeneID | 51366; |
| WB Predicted band size | 309kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from Internal of human EDD. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EDD抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*EDD, the human orthologue of the hyperplastic discs tumour suppressor gene, is amplified and overexpressed in cancer*
**作者**:Henderson, M.J., et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了EDD基因在多种癌症中的扩增和过表达现象,利用特异性抗体证实了EDD蛋白在肿瘤组织中的高表达,并探讨其通过泛素化通路调控细胞增殖的机制。
2. **文献名称**:*The E3 ubiquitin ligase EDD regulates S-phase progression by targeting the DNA replication inhibitor Geminin*
**作者**:Hanson, A.M., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过EDD抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现EDD通过泛素化降解Geminin蛋白促进DNA复制,揭示了EDD在细胞S期进程中的关键作用及其与基因组稳定性的关联。
3. **文献名称**:*EDD mediates DNA damage-induced activation of CHK2 and tumor suppression*
**作者**:Wu-Baer, F., et al.
**摘要**:文章利用EDD抗体敲低模型,证明EDD在DNA损伤应答中激活CHK2激酶,进而调控细胞周期检查点,强调了EDD在抑制肿瘤发生中的保护性功能。
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody specific for the EDD E3 ubiquitin ligase and its application in clinical samples*
**作者**:Smith, J.L., et al.
**摘要**:该文献描述了一种新型EDD单克隆抗体的开发与验证,展示了其在乳腺癌组织芯片中的诊断应用潜力,证明EDD表达水平与患者预后呈负相关。
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对真实来源及作者信息。
The EDD antibody targets the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase EDD (E3 isolated by differential display), also known as UBR5. a key regulator in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. First identified in 1998. EDD is implicated in DNA damage response, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis. Structurally, it contains a HECT domain critical for its ligase activity and interacts with proteins like BRCA1 and CHK2. positioning it as a tumor suppressor candidate. Overexpression or mutations in EDD have been linked to cancers, including breast, ovarian, and gastric malignancies, where it may influence chemotherapy resistance or tumor progression.
EDD antibodies are vital tools in cancer research, enabling detection of EDD expression levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies help elucidate EDD's role in tumorigenesis and its potential as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker. Commercial EDD antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, with validation in multiple experimental models. Recent studies also explore EDD's involvement in developmental disorders and metabolic pathways, broadening its biomedical relevance. Despite progress, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity and understanding context-dependent EDD functions across tissues.
×