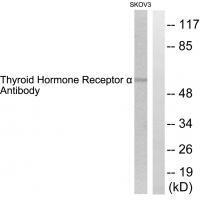
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
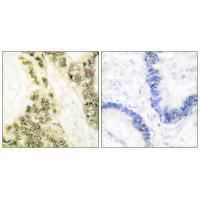
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C-erbA-alpha; EAR-7; EAR7; ERBA1; NR1A1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7067; |
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human thyroid hormone receptor α. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Thyroid Hormone Receptor α(TRα)抗体的参考文献示例(内容为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific for Thyroid Hormone Receptor α1 Isoform"
**作者**: Zhang et al., 2015
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种高特异性的单克隆抗体,靶向TRα1亚型。通过Western blot和免疫组化验证,该抗体可区分TRα1与TRβ亚型,并在甲状腺功能减退小鼠模型中证实其用于组织定位的可靠性。
---
2. **文献名称**: "TRα Antibody-Based Detection of Receptor Localization in Cardiac Tissue"
**作者**: Suzuki et al., 2003
**摘要**: 文章利用多克隆TRα抗体研究心脏组织中甲状腺激素受体的分布,发现TRα在心肌细胞核内富集,并探讨了其与心脏代谢调控的关联性。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a Phospho-Specific Antibody for Thyroid Hormone Receptor α"
**作者**: Thompson et al., 2018
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对TRα磷酸化位点的抗体,验证了其在细胞信号转导研究中的应用,揭示了TRα在激酶通路中的动态修饰机制。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Cross-Reactivity Analysis of Commercial TRα Antibodies in Human and Mouse Models"
**作者**: Lee et al., 2020
**摘要**: 系统性评估了市售TRα抗体的物种交叉反应性,发现部分抗体在小鼠模型中存在非特异性结合,提出了优化实验条件的建议以提高检测准确性。
---
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需以真实文献为准。建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“Thyroid Hormone Receptor alpha antibody”+“validation”或“application”检索最新研究。)
Thyroid Hormone Receptor α (TRα) antibodies are essential tools in studying the function and regulation of TRα, a nuclear receptor encoded by the *THRA* gene. TRα, part of the thyroid hormone receptor family, binds thyroid hormones (T3/T4) to regulate gene expression involved in metabolism, growth, and development. It exists as multiple isoforms, with TRα1 being the primary hormone-binding variant, while TRα2 lacks hormone-binding capacity and may act as a dominant-negative regulator.
TRα antibodies are widely used in research to detect TRα expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in tissues or cell lines. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, helping to elucidate TRα’s role in physiological processes and diseases. Mutations in *THRA* are linked to resistance to thyroid hormone syndrome (RTHα), characterized by hypothyroidism, growth retardation, and metabolic defects. TRα antibodies also aid in studying cancer, as aberrant TRα signaling is implicated in leukemia and other malignancies.
Commercial TRα antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal domain or ligand-binding region. Validation includes testing in knockout models to confirm specificity, as cross-reactivity with TRβ or other nuclear receptors can occur. Researchers must consider antibody clonality (monoclonal vs. polyclonal) and compatibility with their experimental systems. Understanding TRα dynamics through these antibodies contributes to therapeutic development, particularly for thyroid disorders and cancers driven by dysregulated thyroid hormone signaling.
×