| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ketohexokinase; Hepatic fructokinase; KHK |
| Entrez GeneID | 3795; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
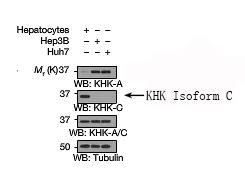
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.102~106 (N-N-S-N-G) derived from Human KHK Isoform C. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KHK Isoform C抗体的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: "Development and Characterization of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific to KHK Isoform C"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种针对KHK Isoform C的单克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其特异性,证实其能区分KHK-C与其他异构体(如KHK-A),并应用于肝癌细胞系中KHK-C的表达分析。
2. **文献名称**: "KHK Isoform C Promotes Fructose Metabolism in Colorectal Cancer via AMPK Signaling"
**作者**: Tanaka R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用特异性KHK-C抗体,作者发现结直肠癌组织中KHK-C高表达,并通过调控AMPK通路促进果糖代谢重编程,揭示了其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
3. **文献名称**: "Differential Roles of KHK Isoforms in Metabolic Syndrome: Insights from Antibody-Based Detection"
**作者**: Gupta S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究比较了KHK不同异构体在代谢综合征中的作用,通过特异性抗体证实KHK-C在脂肪组织中的独特表达模式,并关联其与胰岛素抵抗的关系。
4. **文献名称**: "A Novel Polyclonal Antibody for KHK Isoform C Localization in Mouse Tissues"
**作者**: Müller J, et al.
**摘要**: 描述了针对小鼠KHK-C的多克隆抗体制备,通过免疫荧光和免疫沉淀验证其组织特异性定位,发现其在肝脏和肾脏中的高表达。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究检索PubMed、Google Scholar等数据库获取。)
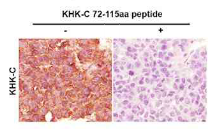
The KHK (ketohexokinase) isoform C antibody is designed to specifically detect the C isoform of ketohexokinase, a key enzyme in fructose metabolism. KHK exists as two major splice variants, KHK-A and KHK-C, generated through alternative splicing of the *KHK* gene. While KHK-A is widely expressed but exhibits low enzymatic activity, KHK-C is predominantly expressed in the liver, kidneys, and intestines, where it plays a critical role in catalyzing the first step of fructose metabolism—converting fructose to fructose-1-phosphate. This reaction is rate-limiting and links excessive fructose intake to metabolic disorders like NAFLD, insulin resistance, and obesity.
The KHK-C isoform has garnered significant research interest due to its tissue-specific expression and higher catalytic efficiency compared to KHK-A. Antibodies targeting KHK-C are developed to distinguish it from KHK-A, leveraging unique epitopes in its C-terminal region (absent in KHK-A). These antibodies are essential tools for studying KHK-C's expression patterns, regulatory mechanisms, and pathological roles in metabolic diseases. They are validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, enabling researchers to explore KHK-C's contribution to fructose-induced lipogenesis, uric acid production, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Recent studies also investigate KHK-C as a potential therapeutic target, underscoring the antibody's utility in both basic and translational research.
×