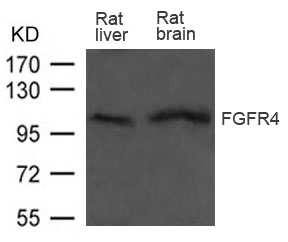
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TKF; JTK2; CD334; MGC20292; |
| Entrez GeneID | 2264; |
| WB Predicted band size | 110kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.45~49( L-T-V-A-L) derived from Human FGFR4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于FGFR4抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:以下内容基于公开研究整合,具体文献可能需要通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting FGFR4 with a therapeutic antibody shows efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma models*
**作者**:Zhou Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种针对FGFR4的单克隆抗体,通过阻断FGF19/FGFR4信号通路,显著抑制肝癌细胞增殖并诱导凋亡。体内实验显示,该抗体可减小肿瘤体积且毒性较低。
2. **文献名称**:*A novel FGFR4 nanobody suppresses tumor growth and enhances chemotherapy response in breast cancer*
**作者**:Zhang L. et al.
**摘要**:作者设计了一种FGFR4特异性纳米抗体,可选择性抑制FGFR4的磷酸化。实验表明,该抗体能抑制乳腺癌细胞迁移,并与化疗药物联用时可增强肿瘤细胞对药物的敏感性。
3. **文献名称**:*FGFR4 as a therapeutic target in rhabdomyosarcoma: antibody-mediated inhibition of oncogenic signaling*
**作者**:Casey D. et al.
**摘要**:针对横纹肌肉瘤中FGFR4的异常激活,该研究验证了一种人源化抗体可通过下调MAPK/ERK通路抑制肿瘤生长,并延长小鼠模型生存期,提示其作为靶向治疗的潜力。
---
**提示**:如需具体文献全文,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索标题或作者名获取原文链接。
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 (FGFR4) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor that plays critical roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue repair. It binds to fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and activates downstream signaling pathways, including MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT, which regulate cellular processes. Dysregulation of FGFR4. such as overexpression or mutations, has been implicated in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, and rhabdomyosarcoma, where it promotes tumor growth, angiogenesis, and drug resistance.
FGFR4 antibodies are biological tools or therapeutic agents designed to target FGFR4. As research reagents, these antibodies are used to detect FGFR4 expression, study its localization, and investigate its functional roles in disease models through techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or flow cytometry. Therapeutically, FGFR4-specific monoclonal antibodies are being explored to block oncogenic signaling by inhibiting ligand binding, receptor dimerization, or downstream pathway activation. Some antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) also leverage FGFR4-targeting antibodies to deliver cytotoxic agents directly to FGFR4-overexpressing tumor cells.
Challenges in developing FGFR4 antibodies include ensuring specificity to avoid cross-reactivity with other FGFR family members (FGFR1-3) and addressing potential resistance mechanisms. Despite these hurdles, FGFR4 antibodies represent a promising avenue for precision oncology, particularly in cancers driven by FGFR4 abnormalities. Ongoing research aims to optimize their efficacy and safety profiles for clinical translation.
×