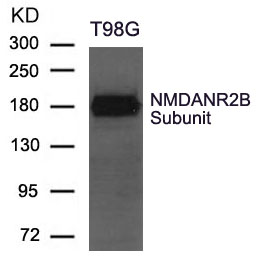
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NMDAR2B; NR2B; |
| Entrez GeneID | 24410; |
| WB Predicted band size | 180kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around aa.1250-1254(N-L-Y-D-I) derived from Human NMDANR2B Subunit. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **NMDAR NR2B亚基抗体** 的3篇参考文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors"*
**作者**:Monyer, H., Burnashev, N., Laurie, D. J., Sakmann, B., & Seeburg, P. H.
**摘要**:研究通过抗体和原位杂交技术揭示了NR2B亚基在大脑发育早期高表达,并随年龄增长逐渐被其他亚基(如NR2A)替代,提示其在突触可塑性中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity"*
**作者**:Liu, L., Wong, T. P., Pozza, M. F., et al.
**摘要**:利用NR2B特异性抗体阻断实验,证明该亚基对长时程增强(LTP)和长时程抑制(LTD)的调控至关重要,并揭示其与学习记忆的分子关联。
3. **文献名称**:*"Selective upregulation of the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor in Alzheimer's disease"*
**作者**:Hynd, M. R., Scott, H. L., & Dodd, P. R.
**摘要**:通过免疫组织化学和Western blot分析,发现阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中NR2B亚基表达异常升高,提示其与疾病中兴奋性毒性损伤的相关性。
---
这些研究均通过NR2B抗体验证了该亚基在生理及病理状态下的功能或分布变化。如需更多文献,可进一步指定应用场景(如疾病模型、技术方法等)。
The NMDAR2B (GluN2B) subunit is a critical component of NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors, a subclass of ionotropic glutamate receptors essential for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. These receptors are heterotetramers, typically composed of two GluN1 subunits and two GluN2 subunits (e.g., GluN2B). The GluN2B subunit confers distinct functional properties to the receptor, including high calcium permeability and prolonged channel-opening kinetics, which influence synaptic signaling and long-term potentiation (LTP). It is highly expressed during early brain development and remains prevalent in regions like the forebrain and hippocampus in adults, though its levels decline with age.
Antibodies targeting the GluN2B subunit are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction with postsynaptic density proteins (e.g., PSD-95) in neurological research. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to investigate NMDA receptor composition and signaling pathways. Dysregulation of GluN2B-containing receptors is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), stroke, and psychiatric disorders (e.g., depression), making these antibodies valuable for exploring disease mechanisms or therapeutic targets. Specificity validation is crucial, as cross-reactivity with other GluN2 subunits (e.g., GluN2A) can confound results. Research using GluN2B antibodies has also shed light on its role in synaptic scaling, excitotoxicity, and the effects of pharmacological modulators like ifenprodil.
×