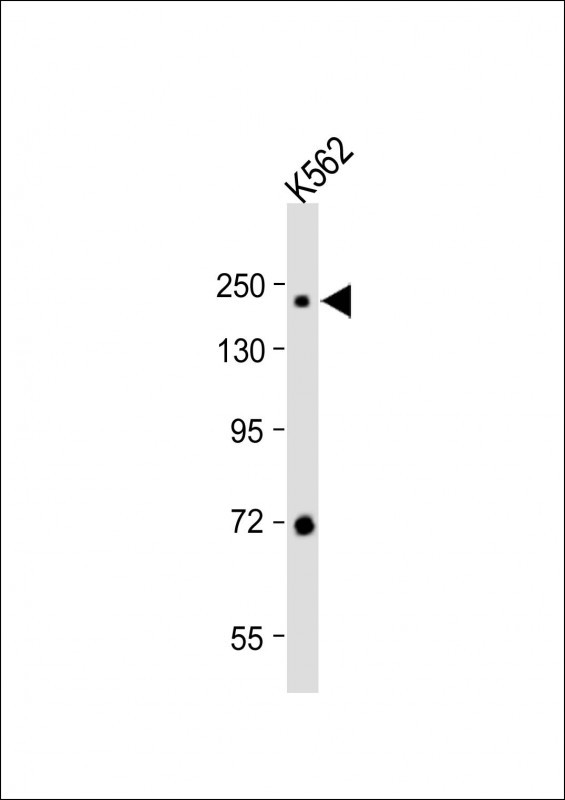
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Histone acetyltransferase KAT6A, MOZ, YBF2/SAS3, SAS2 and TIP60 protein 3, MYST-3, Monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein, Runt-related transcription factor-binding protein 2, Zinc finger protein 220, KAT6A, MOZ, MYST3, RUNXBP2, ZNF220 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7994 |
| WB Predicted band size | 225.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This MOZ/MYST3 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1319-1351 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MOZ/MYST3. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及MOZ/MYST3抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *MOZ regulates the Tbx1 locus, and Moz mutation partially phenocopies DiGeorge syndrome*
**作者**: Voss AK, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用MOZ抗体通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)技术,发现MOZ蛋白通过表观遗传修饰调控Tbx1基因表达,揭示了MOZ缺失导致小鼠模型中出现类似人类DiGeorge综合征的心脏畸形。
---
2. **文献名称**: *The leukemic oncogene MLL–ENL alters transcriptional networks and integrates AML-associated pathways*
**作者**: Wilkinson AC, et al.
**摘要**: 研究中采用MYST3抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证明MLL-ENL融合蛋白与MYST3(MOZ)存在功能互作,共同调控白血病干细胞的关键转录程序,推动急性髓系白血病(AML)的发生。
---
3. **文献名称**: *MOZ is essential for maintaining hematopoietic stem cell function*
**作者**: Katsumoto T, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和流式细胞术结合MOZ特异性抗体,发现MOZ缺失导致造血干细胞自我更新能力丧失,其机制与组蛋白乙酰化介导的Hox基因表达失调相关,为血液系统疾病治疗提供靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请核对数据库(如PubMed)获取完整信息。若需具体文献链接或补充,请进一步说明。
The MOZ/MYST3 antibody targets the MOZ (monocytic leukemia zinc finger protein), also known as KAT6A, a member of the MYST family of histone acetyltransferases (HATs). MOZ plays a critical role in transcriptional regulation, chromatin remodeling, and epigenetic control by acetylating histones, particularly H3K9 and H3K14. to promote gene activation. It is essential for embryonic development, hematopoiesis, and maintaining stem cell pluripotency. MOZ forms complexes with proteins like BRPF1/2/3. ING5. and EAF6. enhancing its enzymatic activity and substrate specificity.
Dysregulation of MOZ is linked to acute myeloid leukemia (AML), often due to chromosomal translocations (e.g., t(8;16) forming MOZ-CBP fusion proteins) that disrupt normal acetylation-dependent transcriptional programs. MOZ mutations are also associated with developmental disorders like Say-Barber-Biesecker-Young-Simpson syndrome.
The MOZ/MYST3 antibody is widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blot, immunoprecipitation, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunofluorescence. It helps investigate MOZ's role in cancer, epigenetics, and cellular differentiation, making it valuable for understanding disease mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Commercial antibodies are typically validated for specificity against the N-terminal or C-terminal regions of MOZ.
×