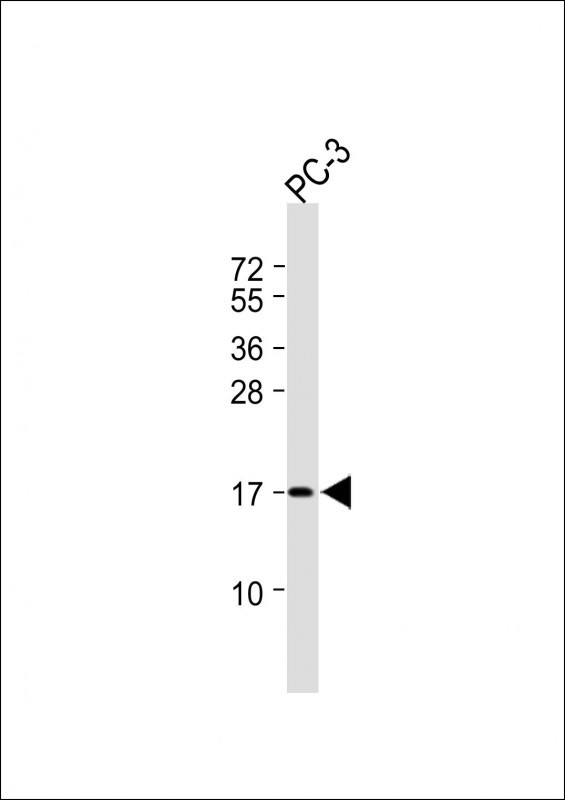

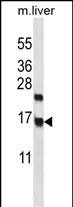
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
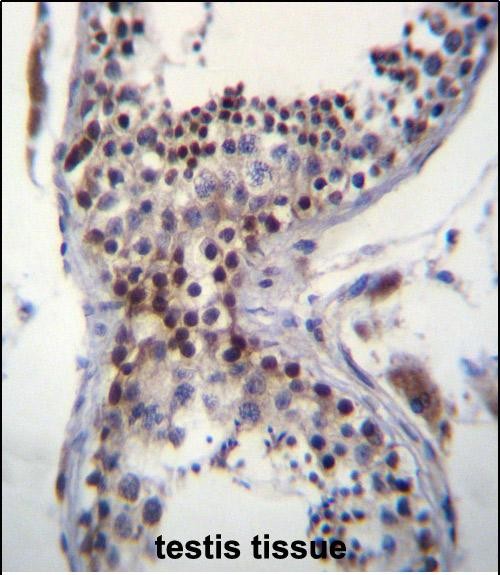
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 58, CCDC58 |
| Entrez GeneID | 131076 |
| WB Predicted band size | 16.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CCDC58 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 5-33 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CCDC58. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CCDC58(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要列表(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *CCDC58 regulates ciliary protein trafficking through interaction with the IFT-B complex*
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对CCDC58 N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,揭示了CCDC58与纤毛内运输复合物IFT-B的相互作用,并证明其在纤毛形成中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Subcellular localization and functional analysis of CCDC58 in mitochondrial dynamics*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫电镜技术(使用CCDC58 N-term抗体),作者发现CCDC58定位于线粒体外膜,并参与线粒体分裂过程的调控,为代谢疾病研究提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Proteomic screening identifies CCDC58 as a novel biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**: Zhang R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究采用CCDC58 N端抗体对肝癌组织进行免疫组化分析,发现CCDC58的高表达与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为肝癌诊断标志物。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例模板,实际引用需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献(可尝试关键词“CCDC58 antibody”或“CCDC58 N-terminal”)。若研究较少,可扩展至相关功能研究(如纤毛、线粒体相关蛋白)或抗体技术文献。
The CCDC58 (N-term) antibody is a tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the coiled-coil domain-containing protein 58 (CCDC58), a less-characterized protein implicated in cellular processes such as cilia formation, cell cycle regulation, and intracellular signaling. CCDC58 contains conserved coiled-coil domains, which mediate protein-protein interactions, suggesting roles in scaffolding or organizing multi-protein complexes. Studies link CCDC58 to centrosomal and ciliary functions, potentially influencing microtubule dynamics and mitotic spindle orientation. Dysregulation of ciliary proteins is associated with developmental disorders and cancers, though CCDC58's precise mechanisms remain under investigation.
The antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry to map CCDC58 expression, localization, and interactions. Its N-terminal specificity helps distinguish CCDC58 from homologous proteins or isoforms. Researchers utilize this antibody to explore CCDC58's involvement in ciliopathies, cellular division, or signaling pathways. Validation data, such as knockout controls or peptide blocking, are critical to confirm its specificity, given the limited literature on CCDC58. Ongoing research aims to clarify its biological significance and potential as a therapeutic target in cilia-related diseases.
×