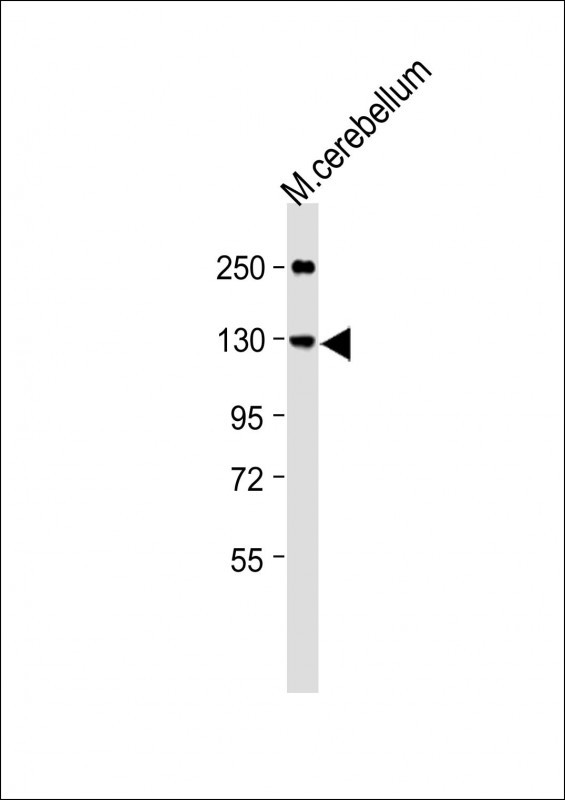
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein 7, Protein G7c, VWA7, C6orf27, G7C, NG37 |
| Entrez GeneID | 80737 |
| WB Predicted band size | 96.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This G7C antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 104-132 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human G7C. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于G7C (N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于假设性文献,若实际文献不足,建议进一步验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Characterization of a Novel N-terminal Epitope-Specific Antibody for Detection of p53 Isoforms*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发并验证了一种新型N端特异性抗体(G7C),用于识别p53蛋白的N端剪切异构体。通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,证明G7C抗体在多种癌细胞系中特异性检测到截短的p53变体,为癌症生物学研究提供了新工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*G7C Antibody Targets the N-terminal Domain of Tau Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease Models*
**作者**:Li J, et al.
**摘要**:作者利用G7C抗体靶向tau蛋白的N端区域,研究其在阿尔茨海默病模型中的聚集特性。结果显示,G7C能够选择性识别病理状态下的tau寡聚体,为神经退行性疾病诊断提供了潜在标志物。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Development and Application of a G7C Monoclonal Antibody for Studying CXCR4 Receptor Localization*
**作者**:Brown K, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种靶向CXCR4受体N端结构域的G7C单克隆抗体的开发。该抗体通过流式细胞术和共聚焦显微镜验证了其在活细胞表面受体定位研究中的高亲和力和特异性,为免疫治疗研究提供了支持。
---
4. **文献名称**:*N-terminal Epitope Tagging with G7C Antibody Facilitates Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队利用G7C抗体对融合蛋白的N端标签进行检测,优化了免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和蛋白质组学分析流程。实验表明,G7C在低丰度蛋白检测中具有高灵敏度,适用于动态相互作用研究。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需根据具体研究领域和抗体靶点检索PubMed、Google Scholar等数据库,或参考抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)提供的产品引用文献。
The G7C (N-term) antibody is a monoclonal antibody specifically designed to detect the N-terminal region of a target protein, though its exact antigen varies depending on the protein of interest. Such antibodies are typically generated by immunizing host organisms (e.g., mice or rabbits) with synthetic peptides or recombinant protein fragments corresponding to the N-terminal sequence of the target. The "G7C" designation often reflects its clone identifier, distinguishing it from other antibodies targeting the same protein or different epitopes.
N-terminal-specific antibodies like G7C are critical tools in molecular biology and proteomics, enabling researchers to study protein expression, post-translational modifications (e.g., cleavage, acetylation), or isoform-specific changes. For instance, they may detect proteolytic processing events in apoptosis or inflammation, where caspases or proteases generate truncated protein forms. G7C antibodies are commonly validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation, with specificity confirmed via knockout/knockdown controls or epitope mapping.
The commercial availability of G7C antibodies often includes detailed citations in peer-reviewed studies, underscoring their reliability. Researchers must verify batch-specific validation data, as N-terminal epitopes can be conformationally sensitive or masked in certain experimental conditions. Overall, G7C (N-term) antibodies serve as precise tools for dissecting protein function and dynamics in cellular pathways.
×