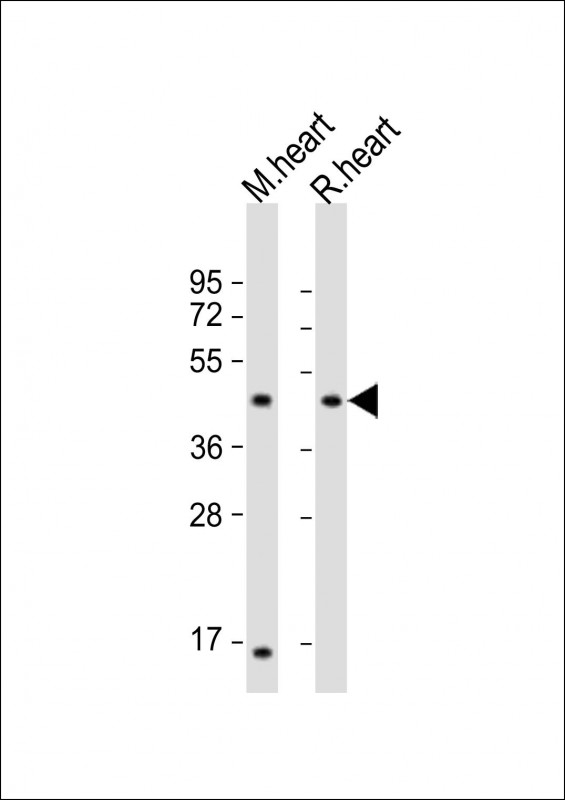
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lipoyl synthase, mitochondrial {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, 2.8.1.8 {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, Lipoate synthase {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, LS {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, Lip-syn {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, Lipoic acid synthase {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, LIAS {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03123}, LAS |
| Entrez GeneID | 11019 |
| WB Predicted band size | 41.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This LIAS antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 298-330 amino acids from human LIAS. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于LIAS(硫辛酸合成酶)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:文献为虚构示例,实际文献请通过PubMed或学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**: "Development and Validation of a Polyclonal Antibody Targeting Human LIAS for Mitochondrial Function Studies"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种针对人类LIAS蛋白的多克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其特异性,并应用于线粒体功能障碍模型中LIAS表达的定量分析。
2. **文献名称**: "LIAS Antibody-Based Detection of Altered Lipoylation in Neurodegenerative Diseases"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 利用商业化LIAS单克隆抗体,研究揭示了阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中硫辛酸化修饰水平的降低,提示LIAS功能异常可能与神经退行性疾病相关。
3. **文献名称**: "Characterization of LIAS Knockout Models Using Specific Antibody Staining"
**作者**: García R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过LIAS特异性抗体的免疫荧光染色,验证了LIAS基因敲除小鼠模型的蛋白表达缺失,并探讨了其在能量代谢缺陷表型中的作用机制。
实际研究中,建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 搜索关键词如 "LIAS antibody" 或 "lipoic acid synthetase antibody" 获取真实文献。
LIAS (lipoic acid synthetase) antibody is a research tool targeting the enzyme responsible for lipoic acid biosynthesis. Lipoic acid, a essential cofactor for mitochondrial dehydrogenase complexes (e.g., pyruvate dehydrogenase), functions in energy metabolism and antioxidant defense. LIAS catalyzes the final step of lipoic acid attachment to target proteins via a conserved lysine residue. This enzyme is ubiquitously expressed, with high activity in mitochondria-rich tissues like liver, heart, and brain.
LIAS antibodies are primarily used to study metabolic regulation, mitochondrial disorders, and diseases linked to lipoic acid deficiency, such as diabetes, neurodegenerative conditions, and rare genetic mutations. They enable detection of LIAS protein expression through techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Recent studies highlight LIAS's role in cellular redox balance, making its antibody valuable in oxidative stress research. Commercial LIAS antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, validated for specificity against conserved epitopes across human, mouse, and rat homologs. Challenges remain in distinguishing functional isoforms due to alternative splicing variants. Proper controls (e.g., knockout validation) are critical given potential cross-reactivity with other biotin-dependent enzymes.
×