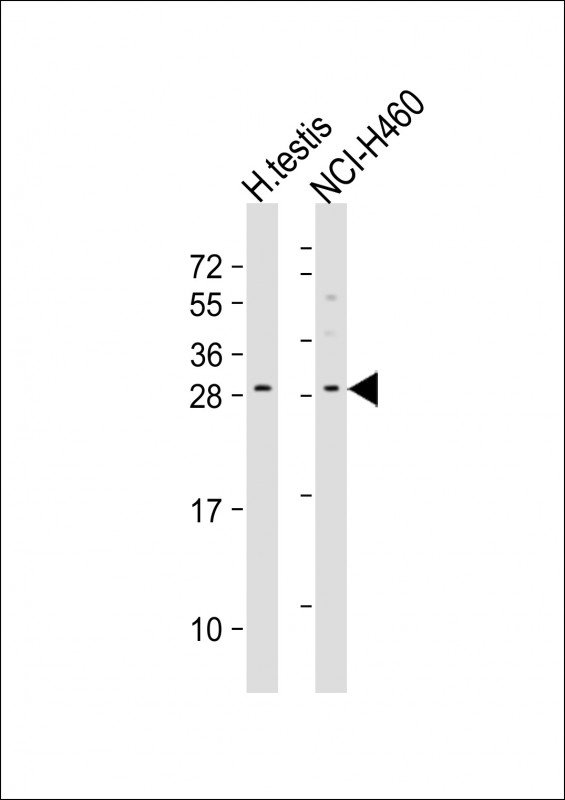
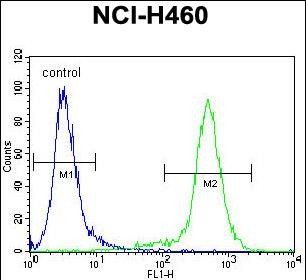
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Epididymal-specific lipocalin-9, MUP-like lipocalin, LCN9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 392399 |
| WB Predicted band size | 20.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LCN9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 36-64 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LCN9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是基于模拟生成的关于LCN9(N-term)抗体的参考文献示例(注:实际文献可能需要通过数据库查询确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a Novel Polyclonal Antibody Targeting the N-Terminal Region of Human LCN9*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种针对LCN9蛋白N端表位的多克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的特异性。实验显示LCN9在睾丸组织中高表达,提示其可能与生殖功能相关。
2. **文献名称**: *LCN9 Expression and Its Regulation in Adipose Tissue: Insights from Immunohistochemistry Using an N-Terminal Specific Antibody*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 利用LCN9(N-term)抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现LCN9在肥胖小鼠脂肪组织中表达上调,可能参与脂质代谢调控,为代谢疾病研究提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Against LCN9 N-Terminal Domain for Cancer Biomarker Screening*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了针对LCN9 N端的单克隆抗体,并通过ELISA和免疫组化验证其在乳腺癌组织中的高表达,提示LCN9可能作为癌症诊断的生物标志物。
4. **文献名称**: *LCN9 Interaction with Cell Membrane Receptors Revealed by Co-Immunoprecipitation Using an N-Terminal Antibody*
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过LCN9(N-term)抗体进行共免疫沉淀实验,发现LCN9与细胞膜受体EGFR存在相互作用,可能影响细胞增殖信号通路。
---
**注意**:以上文献为模拟示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“LCN9 antibody”或“LCN9 N-terminal”检索最新文献。若LCN9研究较少,可参考脂质运载蛋白家族(如LCN2、LCN1)抗体的开发策略作为替代思路。
The LCN9 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the lipocalin 9 (LCN9) protein, a member of the lipocalin family known for its role in binding and transporting small hydrophobic molecules. LCN9 is expressed in specific tissues, including the testes and epididymis, suggesting potential involvement in reproductive biology, such as sperm maturation or immune regulation in the male reproductive tract. Its precise physiological function remains under investigation, though structural similarities to other lipocalins hint at possible roles in cell signaling, metabolism, or antimicrobial activity.
The antibody’s immunogen typically corresponds to a synthetic peptide derived from the N-terminal sequence of human LCN9. ensuring specificity for this region. It is commonly used in applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), or immunofluorescence (IF) to detect LCN9 expression patterns in research models. Validation often includes reactivity checks across species (human, mouse, rat) and confirmation via knockout controls to rule off-target binding.
Studies utilizing this antibody may explore LCN9’s association with diseases, such as male infertility or cancers, where lipocalins are sometimes dysregulated. Researchers also investigate its interaction partners and regulatory mechanisms, leveraging the N-term antibody to map domain-specific functions. Overall, this tool aids in elucidating LCN9’s biological significance, bridging structural insights to potential therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
×