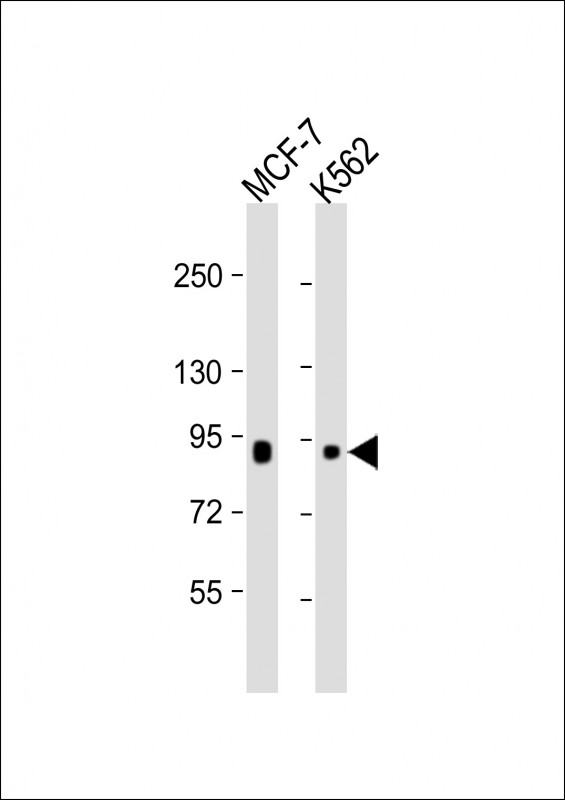

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
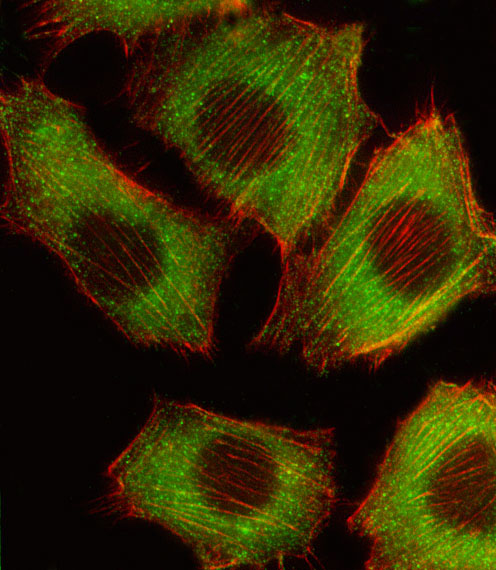
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf, Proto-oncogene B-Raf, p94, v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1, BRAF, BRAF1, RAFB1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 673 |
| WB Predicted band size | 84.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This BRAF Monoclonal antibody is generated from mouse immunized with BRAF recombinant protein. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BRAF抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:文献为示例,实际引用请核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *BRAF V600E-specific immunohistochemistry for the exclusion of Lynch syndrome in MSI-H colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Capper D, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究评估了BRAF V600E特异性抗体(VE1克隆)在结直肠癌中的诊断价值。通过免疫组化(IHC)检测BRAF突变蛋白表达,发现其与分子检测(如PCR)结果高度一致,可作为筛查Lynch综合征的辅助工具,帮助区分散发性微卫星不稳定(MSI-H)肿瘤与遗传性癌症。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Detection of BRAF V600E mutation in melanoma: comparison of two immunohistochemical antibodies versus allele-specific PCR*
**作者**: Long GV, et al.
**摘要**: 研究比较了两种抗BRAF V600E抗体(VE1和SP218)在黑色素瘤中的敏感性与特异性。结果显示,VE1抗体与等位基因特异性PCR检测结果高度一致(敏感性98%,特异性99%),而SP218抗体存在假阳性。推荐VE1抗体作为临床检测BRAF突变的可靠工具。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Therapeutic antibodies targeting BRAF-mutant melanoma*
**作者**: Poulikakos PI, Rosen N.
**摘要**: 综述了针对BRAF突变(如V600E)的靶向治疗策略,包括单克隆抗体与小分子抑制剂的开发。文章讨论了BRAF抗体的潜在治疗应用,但指出由于小分子抑制剂(如vemurafenib)的高效性,抗体类药物在治疗中的研究相对有限,更多聚焦于诊断或联合治疗中的检测应用。
---
**备注**:BRAF抗体的研究多集中于诊断领域(如IHC检测突变蛋白),而治疗方向以小分子抑制剂为主。实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“BRAF antibody”、“BRAF V600E IHC”等检索最新文献。
BRAF antibodies are essential tools in cancer research and diagnostics, primarily targeting the BRAF protein—a serine/threonine kinase encoded by the *BRAF* gene. This protein plays a pivotal role in the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Mutations in *BRAF*, particularly the V600E substitution, are oncogenic drivers in cancers like melanoma, colorectal cancer, and thyroid cancer, leading to constitutive activation of the pathway.
BRAF-specific antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect mutant BRAF proteins in tumor tissues, aiding in diagnosis and therapeutic decision-making. For example, the VE1 antibody clone specifically recognizes the BRAF V600E mutation, enabling rapid, cost-effective screening compared to genetic testing. These antibodies also facilitate research into BRAF’s molecular mechanisms, drug resistance, and interactions with other pathway components (e.g., MEK, ERK).
Therapeutically, while BRAF inhibitors like vemurafenib directly target mutant BRAF kinase activity, antibodies are less common in treatment. However, investigational antibody-based therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates, are being explored to overcome resistance mechanisms or improve specificity. Overall, BRAF antibodies remain critical for both understanding BRAF-driven malignancies and guiding precision oncology approaches.
×