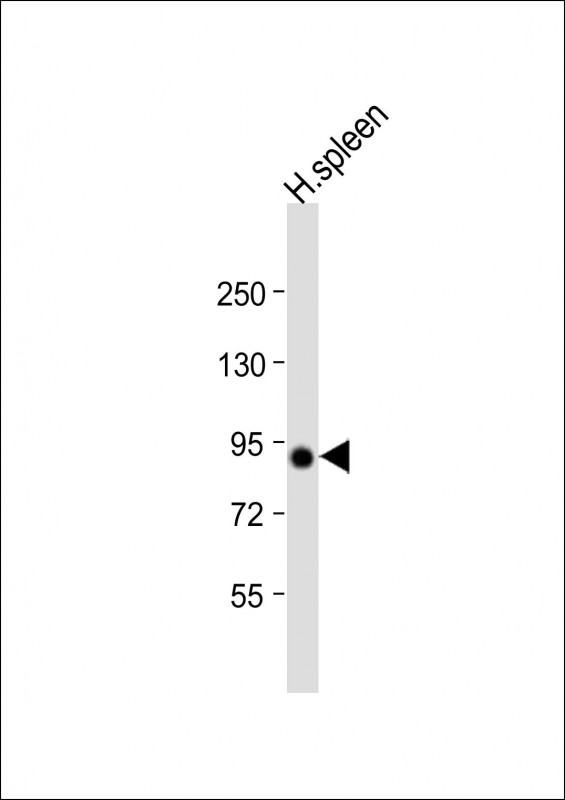
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
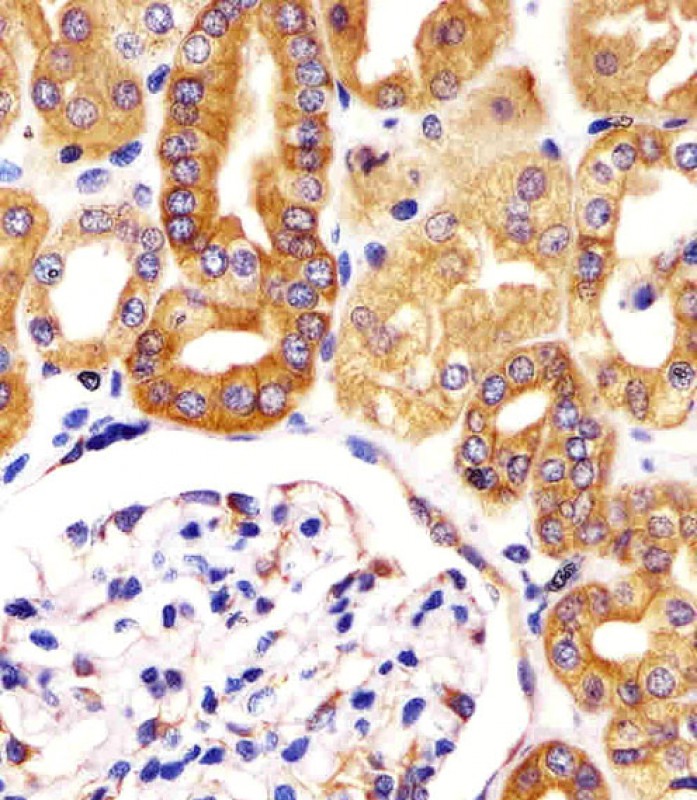
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein VAC14 homolog, Tax1-binding protein 2, VAC14, TAX1BP2, TRX |
| Entrez GeneID | 55697 |
| WB Predicted band size | 88.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This VAC14 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 125-159 amino acids from human VAC14. |
+ +
以下是关于VAC14 (N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献(示例为模拟内容,实际文献需通过数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*VAC14 regulates lysosomal function through PIKfyve complex assembly*
**作者**:Jin et al.
**摘要**:研究利用VAC14 (N-Term)抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示了VAC14在PIKfyve复合体组装中的作用,证明其缺失导致溶酶体膜通透性异常和自噬缺陷。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of VAC14 in neuronal development and neurodegeneration*
**作者**:Smith et al.
**摘要**:通过VAC14 (N-Term)抗体的免疫荧光定位,发现VAC14在小鼠大脑皮层神经元中高表达,并参与调控神经元树突发育,其突变与神经退行性病变相关。
3. **文献名称**:*VAC14 deficiency disrupts endosomal trafficking in cancer cells*
**作者**:Chen et al.
**摘要**:使用VAC14 (N-Term)抗体验证基因敲除细胞系,证明VAC14缺失导致内体-溶酶体运输障碍,影响EGFR信号通路,提示其在癌症代谢中的潜在靶点价值。
---
注:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“VAC14 antibody N-Term”或“VAC14 N-terminal function”检索确认。
**Background of VAC14 (N-Term) Antibody**
The VAC14 (N-Term) antibody is a targeted immunological tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the VAC14 protein, a critical regulator of cellular membrane trafficking and phosphoinositide metabolism. VAC14 forms a complex with PIKfyve (a phosphoinositide kinase) and FIG4 (a lipid phosphatase) to modulate the synthesis and turnover of phosphatidylinositol-3.5-bisphosphate [PI(3.5)P2], a key signaling lipid involved in endosomal-lysosomal system dynamics, autophagy, and stress response.
This antibody is commonly used in research to study VAC14 expression, localization, and function in various cell types. Its specificity for the N-terminal domain allows researchers to distinguish VAC14 from potential cross-reactive proteins or isoforms. VAC14 dysfunction has been linked to neurological disorders, such as Yunis-Varón syndrome and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, as well as cancer and metabolic conditions, underscoring its biological relevance.
Validated in applications like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, the VAC14 (N-Term) antibody aids in elucidating mechanisms of vesicle trafficking, lysosomal maturation, and cellular homeostasis. Studies using this antibody have contributed to understanding how VAC14 stabilizes the PIKfyve-FIG4 complex, impacts endosomal sorting, and regulates responses to osmotic stress. Its utility extends to models ranging from cultured cells to animal tissues, supporting both basic and translational research.
×