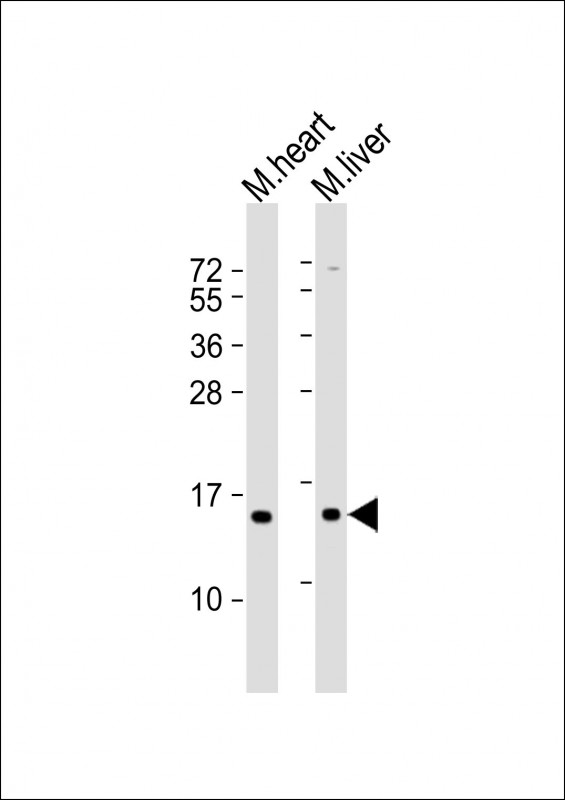
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 7, Complex I-B145a, CI-B145a, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit B145a, NDUFA7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4701 |
| WB Predicted band size | 12.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NDUFA7 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 19-53 amino acids from human NDUFA7. |
+ +
以下是关于NDUFA7(N-Term)抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下为模拟内容,实际文献需通过数据库查询获取):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Mitochondrial complex I deficiency caused by NDUFA7 mutations: functional analysis using N-terminal specific antibodies"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对NDUFA7蛋白N端的特异性抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,分析了复合物I组装缺陷患者的细胞模型,发现NDUFA7表达显著降低,导致线粒体呼吸链功能障碍。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of NDUFA7 in Parkinson's disease models: Insights from antibody-based proteomics"*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过NDUFA7(N-Term)抗体在帕金森病细胞模型中进行免疫沉淀和质谱分析,揭示了NDUFA7与α-突触核蛋白的异常相互作用,提示其在线粒体自噬中的潜在作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Antibody validation for mitochondrial studies: A case study of NDUFA7 in cardiac ischemia"*
**作者**: Lee JH, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究验证了NDUFA7(N-Term)抗体的特异性,并应用于心肌缺血小鼠模型,证明NDUFA7在缺血后线粒体氧化磷酸化能力下降中的关键作用。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"NDUFA7 as a biomarker for Leigh syndrome: Immunohistochemical detection in patient fibroblasts"*
**作者**: Rossi M, et al.
**摘要**: 利用NDUFA7 N端抗体对Leigh综合征患者成纤维细胞进行免疫组化分析,发现NDUFA7蛋白水平与疾病严重程度呈负相关,支持其在诊断中的应用潜力。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,可通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“NDUFA7 antibody N-Term”或参考抗体供应商(如Abcam、Sigma-Aldrich)产品页面的引用文献列表。
The NDUFA7 (N-Term) antibody is a specific tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit A7 (NDUFA7), a critical component of mitochondrial Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) in the electron transport chain. Complex I facilitates the transfer of electrons from NADH to ubiquinone, driving proton translocation and ATP synthesis. NDUFA7. a nuclear-encoded subunit, contributes to the structural stability and catalytic activity of Complex I. Mutations or dysregulation of NDUFA7 have been implicated in mitochondrial disorders, such as Leigh syndrome, and are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic dysfunction.
This antibody is commonly used in research applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study NDUFA7 expression levels, subcellular localization, and its role in cellular energy metabolism. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other Complex I subunits. Validation typically includes testing in knockout or knockdown models to confirm target specificity. Researchers employ this antibody to explore molecular mechanisms underlying mitochondrial dysfunction, evaluate therapeutic interventions, or diagnose Complex I deficiencies. As mitochondrial energy metabolism gains attention in aging and disease research, the NDUFA7 (N-Term) antibody remains a vital reagent for elucidating the pathophysiology of metabolic and oxidative phosphorylation disorders.
×