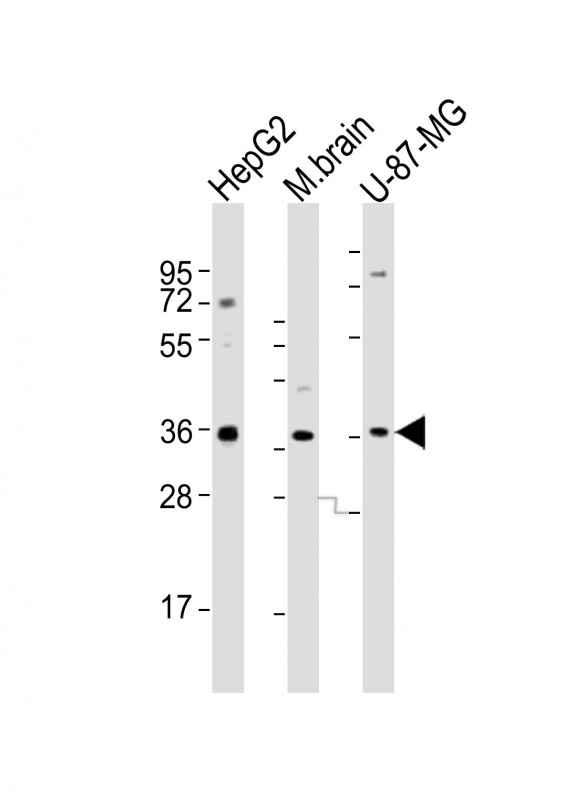
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Quinone oxidoreductase, NADPH:quinone reductase, Zeta-crystallin, CRYZ |
| Entrez GeneID | 1429 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CRYZ antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 248-282 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CRYZ. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及CRYZ(ζ-结晶蛋白)抗体的研究文献摘要,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CRYZ as a novel regulator of angiogenesis in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化(使用CRYZ特异性抗体)发现CRYZ在结直肠癌血管内皮细胞中高表达,并验证其通过调节VEGF信号通路促进肿瘤血管生成。抗体用于组织定位及蛋白水平定量分析。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against ζ-crystallin in age-related cataracts*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CRYZ抗体检测白内障患者晶状体中的自身抗体,发现CRYZ的异常聚集与氧化应激相关,提示其可能作为年龄相关性白内障的生物标志物。抗体用于Western blot和免疫沉淀分析。
---
3. **文献名称**: *CRYZ modulates hepatic lipid metabolism via PPARα signaling*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CRYZ抗体敲低小鼠模型,研究揭示CRYZ通过结合PPARα调控肝脏脂代谢,抗体用于免疫荧光定位及蛋白质相互作用验证,为代谢综合征治疗提供新靶点。
---
如需更多文献或具体应用方向(如神经疾病),可进一步补充关键词筛选。
CRYZ (zeta-crystallin) is a member of the α-crystallin protein family, initially identified as a structural component in the eye lens, where it contributes to maintaining lens transparency and refractive properties. Beyond its role in ocular biology, CRYZ functions as a NADPH-dependent quinone oxidoreductase, participating in cellular detoxification by reducing reactive quinones and modulating oxidative stress. This enzymatic activity links CRYZ to metabolic regulation and redox homeostasis in various tissues, including the liver, kidney, and brain.
CRYZ antibodies are tools used to study the protein's expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. Research has implicated CRYZ in several diseases: mutations are associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataracts, while altered expression is observed in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and cancers, where oxidative stress pathways are dysregulated. Antibodies against CRYZ enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding investigations into its role in disease mechanisms or metabolic syndromes.
Recent studies also explore CRYZ's potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in metabolic disorders linked to insulin resistance. Its dual role as a structural protein and metabolic enzyme makes it a unique subject for interdisciplinary research, bridging ophthalmology, neurology, and oncology. CRYZ antibodies thus serve as critical reagents for deciphering its multifaceted contributions to health and disease.
×