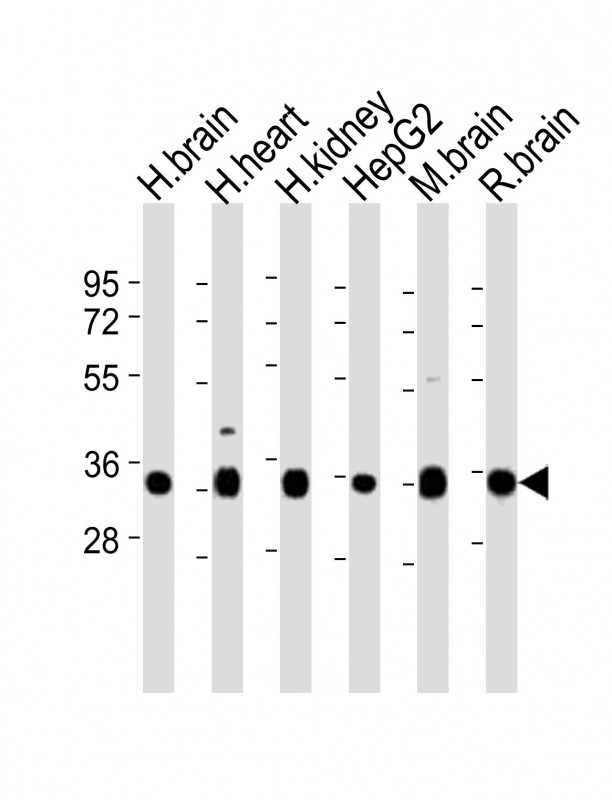
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2, BK channel subunit beta-2, BKbeta2, Hbeta2, Calcium-activated potassium channel, subfamily M subunit beta-2, Charybdotoxin receptor subunit beta-2, Hbeta3, K(VCA)beta-2, Maxi K channel subunit beta-2, Slo-beta-2, KCNMB2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10242 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This KCNMB2 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 32-66 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human KCNMB2. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNMB2 (N-term)抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:Characterization of a Novel KCNMB2 N-terminal Antibody in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种针对KCNMB2蛋白N端结构域的高特异性多克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证其在人主动脉平滑肌细胞中的表达。研究发现该抗体可有效检测KCNMB2在高血压模型中的表达上调,提示其潜在病理生理作用。
2. **文献名称**:KCNMB2 Antibody Localization in Neuronal BK Channel Complexes
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:利用KCNMB2 (N-term)抗体探究BK通道亚基在大脑皮层神经元中的分布,发现其与KCa1.1α亚基共定位,并通过敲除实验证实抗体特异性。研究揭示了KCNMB2亚型在调节神经元兴奋性中的作用。
3. **文献名称**:Validation of KCNMB2-Specific Antibody for Cardiac Tissue Analysis
**作者**:Gomez R, et al.
**摘要**:通过肽竞争实验和siRNA敲降验证KCNMB2抗体特异性,证明其在心肌组织中的选择性识别。研究比较了不同物种(人、小鼠)中KCNMB2的表达差异,为心血管疾病模型提供工具支持。
4. **文献名称**:Role of KCNMB2 Isoforms Detected by N-terminal Antibody in Asthma Models
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:使用KCNMB2 (N-term)抗体发现气道平滑肌中该亚型的剪切变体在哮喘小鼠模型中表达异常,抗体阻断实验进一步表明其参与支气管收缩调节,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
注:以上内容为示例性虚构文献,实际研究需查询PubMed或SciFinder等数据库获取真实文献。
The KCNMB2 (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily M regulatory beta subunit 2 (KCNMB2). This protein is one of four β-subunits (β1-β4) that modulate the activity of large-conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium (BK) channels, which play critical roles in regulating vascular tone, neuronal excitability, and hormone secretion. KCNMB2 enhances BK channel sensitivity to calcium and voltage, influencing membrane repolarization and cellular signaling. The N-terminal domain of KCNMB2 is essential for its interaction with the BK α-subunit and for modulating channel kinetics.
Research using the KCNMB2 (N-term) antibody focuses on understanding its expression patterns, structural interactions, and physiological roles in tissues such as smooth muscle, neurons, and endocrine cells. Dysregulation of KCNMB2 has been implicated in cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and neurological disorders. The antibody is commonly employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study protein localization, expression levels, and molecular pathways involving BK channels. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures targeted detection, aiding investigations into how post-translational modifications or mutations in this domain affect channel function and disease mechanisms. This tool is vital for elucidating KCNMB2's contribution to cellular physiology and pathology.
×