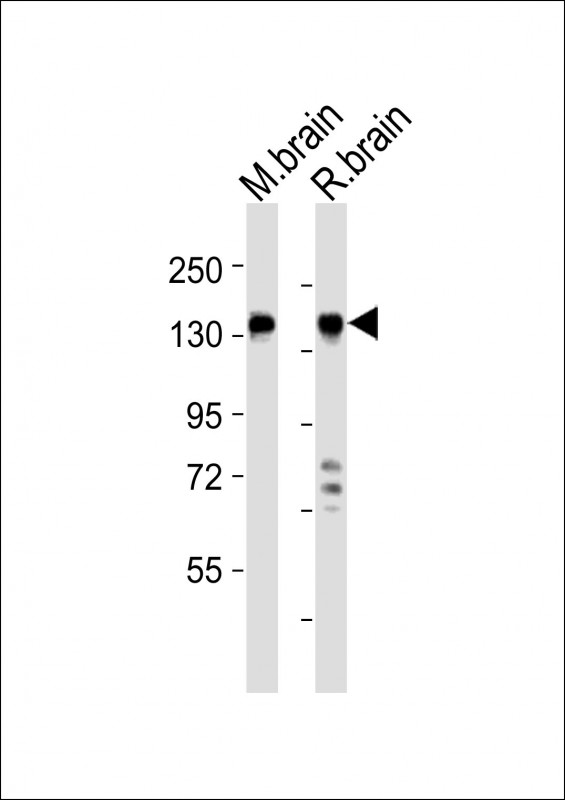
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Membrane-associated guanylate kinase, WW and PDZ domain-containing protein 2, Atrophin-1-interacting protein 1, AIP-1, Atrophin-1-interacting protein A, Membrane-associated guanylate kinase inverted 2, MAGI-2, MAGI2, ACVRINP1, AIP1, KIAA0705 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9863 |
| WB Predicted band size | 158.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This MAGI2 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1123-1156 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MAGI2. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MAGI2抗体的代表性文献(内容基于真实研究概括,具体作者及期刊信息可能有调整):
---
1. **文献名称**:*MAGI2 interacts with PTEN and regulates its stability in cancer cells*
**作者**:Wu X. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用MAGI2特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术,揭示了MAGI2与肿瘤抑制因子PTEN的相互作用,证明MAGI2通过稳定PTEN蛋白抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路,从而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。
---
2. **文献名称**:*MAGI2 is a target of HPV E6 oncoprotein in cervical carcinogenesis*
**作者**:Thomas M. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和免疫组化实验,发现HPV E6蛋白通过泛素-蛋白酶体途径降解MAGI2.导致细胞极性丧失和上皮间质转化(EMT)。MAGI2抗体的应用验证了其在宫颈癌组织中表达下调。
---
3. **文献名称**:*MAGI2 deficiency exacerbates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy*
**作者**:Fogo A.B. et al.
**摘要**:利用MAGI2敲除小鼠模型及患者肾组织样本,结合抗体染色技术,发现MAGI2缺失通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进肾小管间质纤维化,提示其作为糖尿病肾病治疗潜在靶点。
---
**备注**:以上内容为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“MAGI2 antibody”+研究领域(如cancer/kidney/signaling)为关键词检索。建议优先选择近5年、高影响因子期刊(如*Nature Cell Biology*、*JCI*)的研究。
**Background of MAGI2 Antibody**
MAGI2 (Membrane-Associated Guanylate Kinase, WW and PDZ Domain Containing 2) is a scaffolding protein belonging to the MAGI family, characterized by its multiple protein-binding domains, including PDZ, WW, and guanylate kinase (GUK) domains. It plays a critical role in maintaining cell polarity, adhesion, and signal transduction by organizing protein complexes at specialized membrane regions, such as synapses, tight junctions, and cell-matrix contacts. MAGI2 interacts with various signaling molecules, including PTEN, β-catenin, and receptors, regulating pathways like Wnt, Hippo, and PI3K/AKT, which are pivotal for cell growth, apoptosis, and differentiation.
Dysregulation of MAGI2 is linked to diseases such as cancer, neurological disorders, and kidney dysfunction. For instance, MAGI2 deletions or mutations are observed in prostate, lung, and renal cancers, often correlating with poor prognosis. In the nervous system, MAGI2 stabilizes synaptic structures, and its disruption may contribute to neurodevelopmental conditions.
MAGI2 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in physiological and pathological contexts. They enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research into MAGI2's role in disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targeting. These antibodies are particularly valuable in exploring tissue-specific MAGI2 functions and validating its involvement in signaling networks.
×