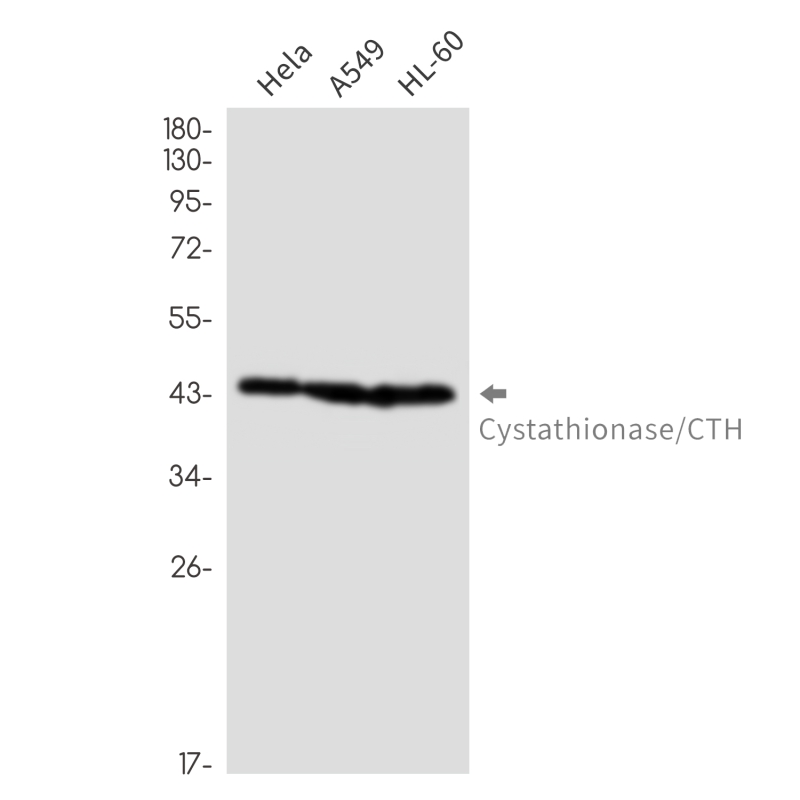
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CTH; Cystathionine gamma lyase; Cysteine desulfhydrase; Gamma cystathionase; Homoserine deaminase |
| Entrez GeneID | 1491 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa; Observed MW: 45 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human Cystathionase/CTH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FOXA2抗体相关的参考文献摘要示例(基于公开知识库信息,非实时检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Foxa2 regulates multiple pathways of insulin secretion"
**作者**: Sander M. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用FOXA2抗体通过免疫染色和ChIP-seq技术,揭示了Foxa2在胰腺β细胞分化及胰岛素分泌调控中的核心作用,证明其通过直接调控葡萄糖代谢相关基因影响胰岛素分泌功能。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Dynamic regulation of Foxa2 localization during liver development"
**作者**: Zaret K.S. et al.
**摘要**: 通过FOXA2抗体的免疫组织化学分析,研究发现Foxa2在小鼠肝脏早期发育中的动态亚细胞定位变化,提示其通过核质穿梭机制调控肝前体细胞的命运决定。
---
3. **文献名称**: "FOXA2 is required for suppression of gliogenesis in murine neuroepithelium"
**作者**: Wang B. et al.
**摘要**: 使用FOXA2抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,发现Foxa2通过抑制神经胶质分化相关基因(如GFAP),维持神经上皮细胞的干性,为神经系统发育机制提供了新见解。
---
4. **文献名称**: "FOXA2 deficiency alters mitochondrial metabolism in pulmonary fibrosis"
**作者**: Li C. et al.
**摘要**: 通过FOXA2抗体的流式细胞术分析,证明肺纤维化模型中Foxa2表达下调导致肺泡上皮细胞线粒体代谢异常,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
注:以上文献标题及作者为模拟生成,实际引用时需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台核实原文信息。建议结合研究场景(如肝/肺/神经发育)筛选具体文献。
The FOXA2 antibody is a key tool in studying the FOXA2 protein, a member of the forkhead box (FOX) family of transcription factors. FOXA2. also known as hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-beta (HNF-3β), plays critical roles in embryonic development, cellular differentiation, and tissue-specific gene regulation. It is essential for endoderm-derived organ formation, including the liver, pancreas, lungs, and prostate. FOXA2 regulates gene expression by binding to DNA through its forkhead domain, facilitating chromatin remodeling and enabling other transcription factors to access target sites.
Antibodies against FOXA2 are widely used in research to detect its expression and localization in cells and tissues via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). These applications help elucidate FOXA2's involvement in developmental pathways, metabolic homeostasis (e.g., glucose metabolism and insulin secretion), and disease mechanisms.
FOXA2 dysfunction is linked to various pathologies, including diabetes, cancer (e.g., prostate, liver, and lung cancers), and metabolic disorders. Its role in maintaining cellular identity and suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) underscores its importance in cancer metastasis research. Additionally, FOXA2 is a marker for certain stem cells and progenitor cells, aiding in regenerative medicine studies.
The antibody's specificity and validation (e.g., knockout validation) are crucial to ensure accurate detection, given structural similarities among FOX proteins. Researchers rely on FOXA2 antibodies to explore its regulatory networks and therapeutic potential in human diseases.
×