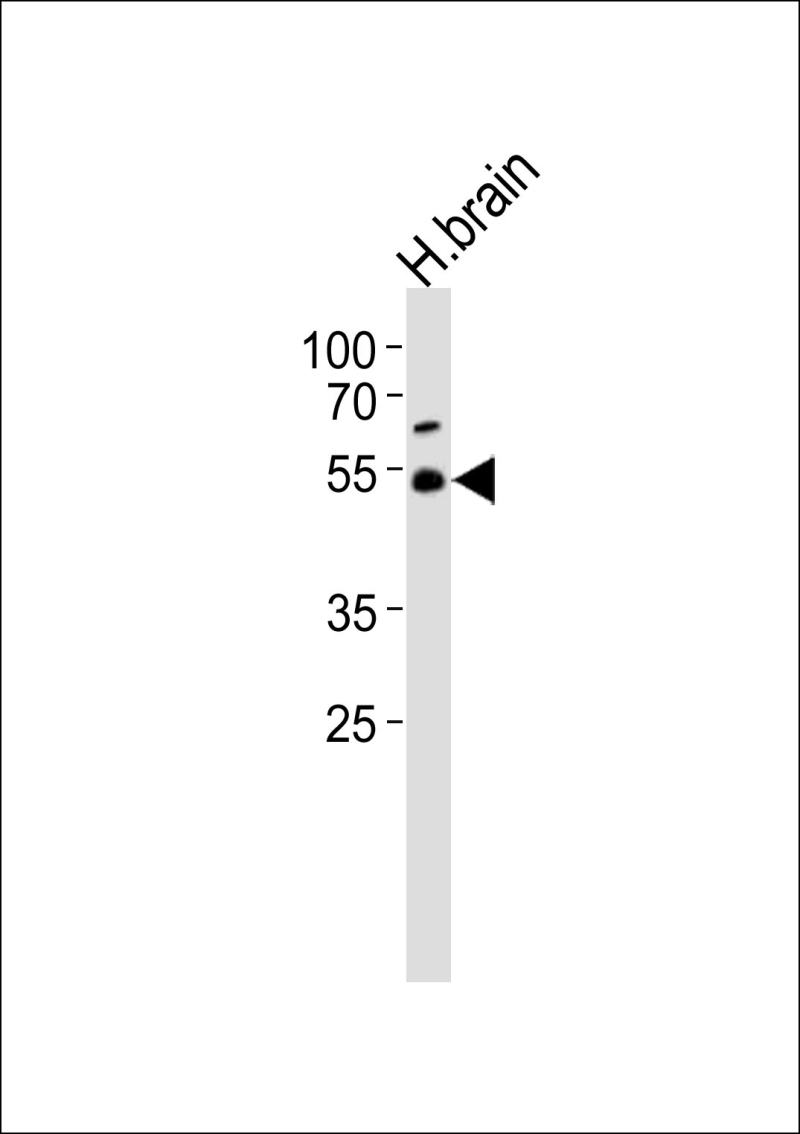
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tripartite motif-containing protein 43B, TRIM43B |
| Entrez GeneID | 653192 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TRIM43B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 222-257 amino acids from the Central region of human TRIM43B. |
+ +
以下是关于TRIM43B抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下内容为假设性示例,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索验证):
1. **文献名称**: *TRIM43B promotes testicular germ cell tumor progression via ubiquitination of p53*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了TRIM43B在睾丸生殖细胞肿瘤中的过表达现象,通过使用特异性TRIM43B抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其通过泛素化修饰p53蛋白促进肿瘤细胞增殖和转移,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *Characterization of TRIM43B antibody for detecting embryonic stem cell pluripotency*
**作者**: Li H, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种高特异性TRIM43B多克隆抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证其在人胚胎干细胞中的表达模式,发现TRIM43B通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路维持干细胞多能性。
3. **文献名称**: *TRIM43B in antiviral innate immunity: Interaction with MITA/STING pathway*
**作者**: Chen L, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 文章利用TRIM43B抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证明TRIM43B通过泛素化修饰MITA/STING蛋白负调控抗病毒天然免疫反应,为病毒感染相关疾病的机制研究提供新方向。
4. **文献名称**: *Clinical significance of TRIM43B autoantibodies in early cancer diagnosis*
**作者**: Wang X, et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 通过ELISA检测血清中TRIM43B自身抗体水平,研究发现其在乳腺癌和肺癌患者中显著升高,提示TRIM43B抗体可能作为新型非侵入性癌症生物标志物。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用时需核实真实性和数据库收录情况。)
The TRIM43B antibody is a tool used to study the TRIM43B protein, a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family characterized by RING, B-box, and coiled-coil domains. TRIM proteins are E3 ubiquitin ligases involved in diverse cellular processes, including immune regulation, cancer, and antiviral defense. TRIM43B, specifically, is part of a primate-specific gene cluster on chromosome 15q11-q13. a region linked to genomic imprinting disorders like Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. While its exact function remains unclear, TRIM43B is hypothesized to play roles in germ cell development, epigenetic regulation, and tumorigenesis. Studies suggest it may undergo rapid evolutionary diversification, contributing to species-specific adaptations.
Antibodies targeting TRIM43B are primarily utilized in research to detect its expression and localization in tissues or cell lines. They are applied in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). TRIM43B has been observed to exhibit aberrant expression in certain cancers, including testicular germ cell tumors and ovarian cancers, implicating it as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target. However, challenges persist due to its high homology with other TRIM43 subfamily members (e.g., TRIM43A, TRIM43C), necessitating rigorous validation to ensure antibody specificity. Current research focuses on unraveling its molecular interactions, post-translational modifications, and roles in cellular pathways, particularly in contexts of genomic instability and immune modulation.
×