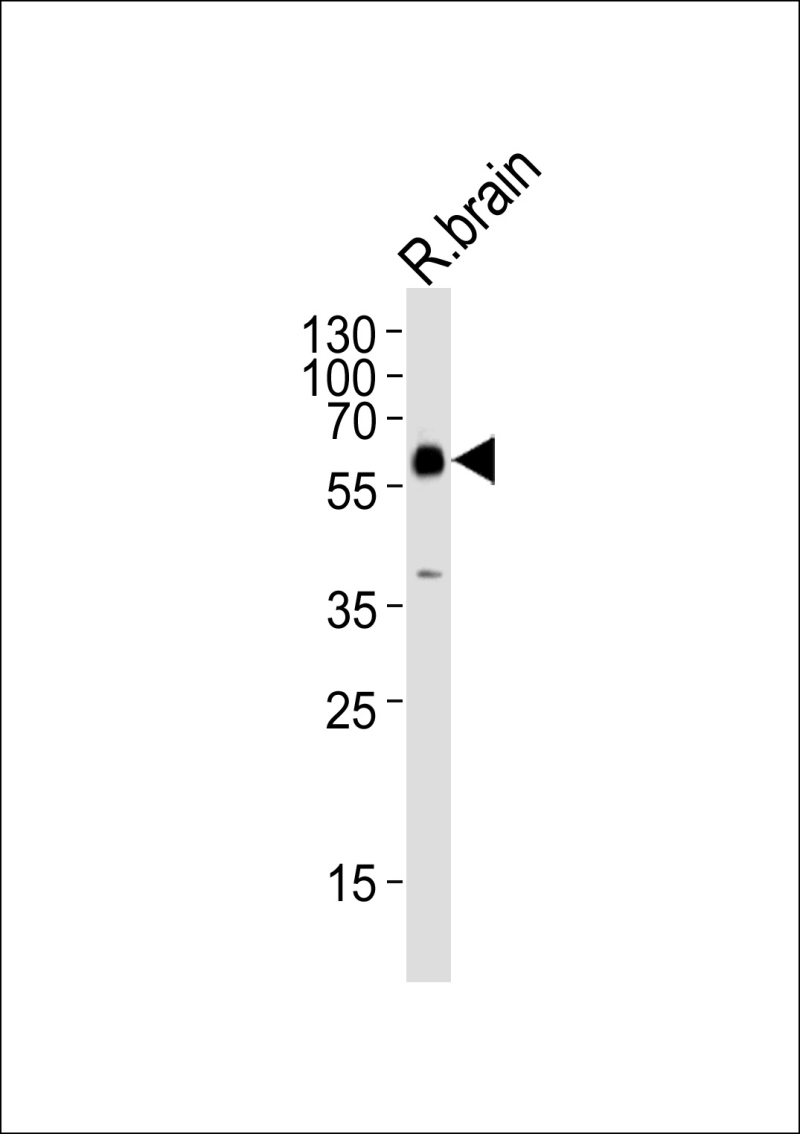


| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
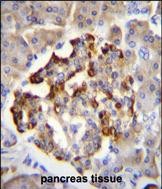
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glutamate decarboxylase 2, 65 kDa glutamic acid decarboxylase, GAD-65, Glutamate decarboxylase 65 kDa isoform, GAD2, GAD65 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2572 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This GAD2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 109-138 amino acids from the Central region of human GAD2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与GAD2抗体相关的研究文献概览:
1. **文献名称**: *GAD65 Autoantibodies in Type 1 Diabetes*
**作者**: Notkins AL, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨GAD65抗体在1型糖尿病中的诊断价值及病理机制,强调其作为胰岛β细胞自身免疫标志物在早期筛查中的应用。
2. **文献名称**: *Stiff-Person Syndrome and GAD Antibodies: Clinical Insights*
**作者**: Dalakas MC.
**摘要**: 分析GAD抗体与僵人综合征(SPS)的关联,发现抗体通过抑制GABA能神经传递导致肌肉强直和痛性痉挛的机制。
3. **文献名称**: *GAD65 Antibodies in Autoimmune Neurological Disorders*
**作者**: Vianello M, et al.
**摘要**: 系统性综述GAD65抗体在多种神经系统自身免疫疾病(如小脑性共济失调、癫痫)中的异质性表现及潜在治疗策略。
4. **文献名称**: *GAD2 Knockout Mice Reveal GABAergic Dysfunction*
**作者**: Kash SF, et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建GAD2基因敲除小鼠模型,揭示GABA合成缺陷导致的神经兴奋性失衡,为研究GAD相关抗体疾病的动物模型提供基础。
(注:以上文献标题及作者为简化示例,实际引用需核对具体文献来源。)
**Background of GAD2 Antibodies**
Glutamic acid decarboxylase 2 (GAD2), also known as GAD65. is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glutamate to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a key inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. GAD2 antibodies (GAD65-Ab) are autoantibodies targeting this enzyme, primarily associated with autoimmune disorders.
In type 1 diabetes (T1D), GAD65-Ab are markers of pancreatic beta-cell destruction, often appearing years before clinical onset. They contribute to autoimmune-mediated insulin deficiency by triggering T-cell responses against beta cells. These antibodies are also linked to rare neurological conditions, such as stiff-person syndrome (SPS) and cerebellar ataxia, where they disrupt GABAergic signaling, leading to motor and cognitive impairments.
GAD65-Ab detection aids in diagnosing autoimmune diabetes (distinguishing T1D from type 2) and neurological syndromes. However, their presence alone isn’t diagnostic, requiring correlation with clinical symptoms. Research explores their pathogenic role and potential therapeutic strategies, including immunomodulation. Despite advances, the exact mechanisms of GAD65-Ab in disease progression remain under investigation, highlighting their complexity in autoimmunity.
×