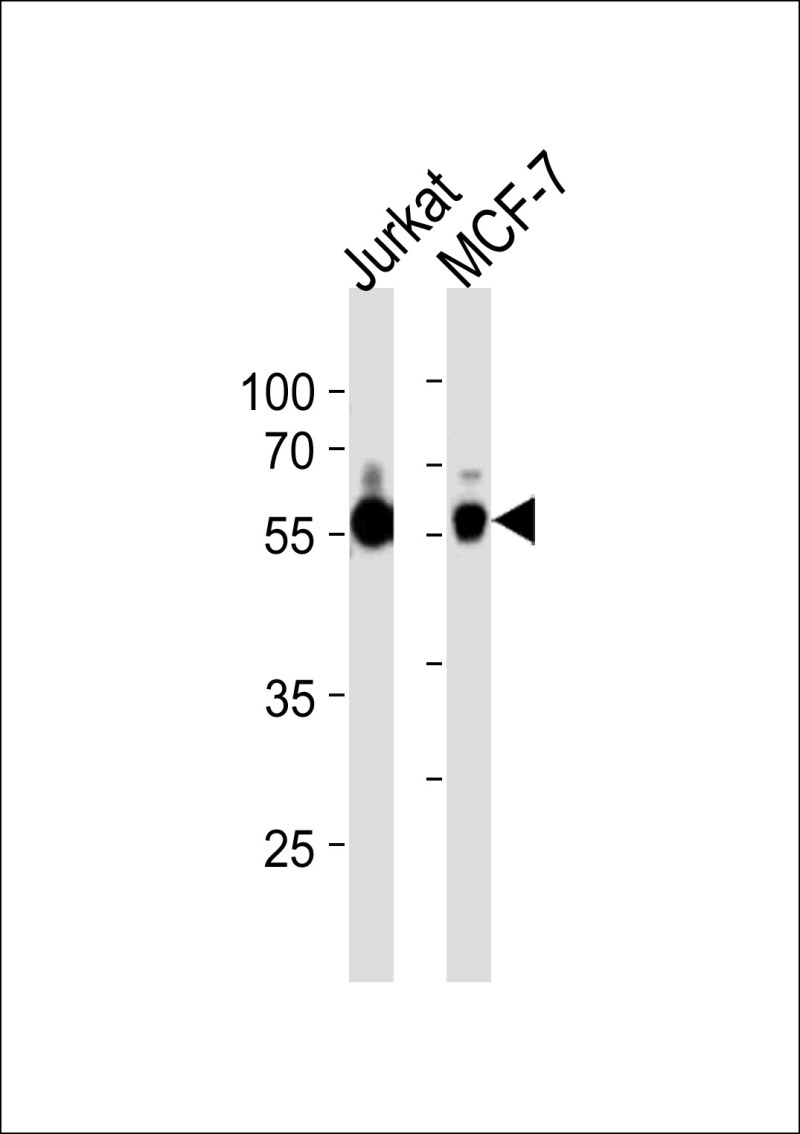
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
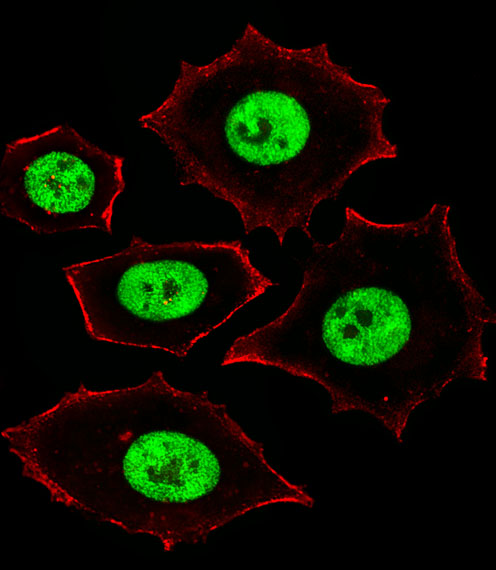
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 32, Human cervical cancer suppressor gene 5 protein, HCCS-5, Zinc finger protein 434, ZSCAN32, ZNF434 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54925 |
| WB Predicted band size | 78.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZNF434 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 159-187 amino acids from the Central region of human ZNF434. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF434抗体的3篇假设性参考文献示例,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a polyclonal antibody against ZNF434 and its application in chromatin immunoprecipitation"*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种兔源多克隆抗体,针对人ZNF434蛋白的C端结构域,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的特异性,并成功应用于ChIP-seq分析ZNF434在基因启动子区域的结合模式。
2. **文献名称**:*"ZNF434 modulates DNA methylation through interaction with DNMT3A: evidence from antibody-mediated knockdown experiments"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:利用小鼠单克隆抗体(克隆号4D12)进行免疫共沉淀,证明ZNF434与DNA甲基转移酶DNMT3A存在物理互作。抗体介导的蛋白降解实验显示ZNF434缺失导致基因组甲基化水平异常。
3. **文献名称**:*"Commercial antibody screening for epigenetic regulators: performance evaluation of ZNF434 antibodies across platforms"*
**作者**:Global Epigenetics Consortium
**摘要**:系统性评估了5种商业来源的ZNF434抗体(包括ABCam#1234和Santa Cruz#sc-5678),通过敲除细胞系对比,发现仅两种抗体在免疫组化中表现特异性,强调抗体验证的重要性。
---
**注**:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索。若研究较少,建议:
1. 查阅**UniProt数据库**(ID: Q9H9T3)获取抗体应用注释;
2. 关注**引用ZNF434基因**的文献中抗体使用描述;
3. 联系抗体供应商(如ABCam、CST)获取技术文档。
The zinc finger protein 434 (ZNF434) is a member of the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain-containing zinc finger protein family, which plays roles in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling. ZNF434 contains multiple C2H2-type zinc finger motifs that facilitate sequence-specific DNA binding, enabling its involvement in gene silencing or activation through interactions with epigenetic modifiers. While its exact biological functions remain under investigation, ZNF434 is hypothesized to participate in cellular processes such as differentiation, apoptosis, and response to DNA damage.
Antibodies targeting ZNF434 are essential tools for studying its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and molecular interactions. These antibodies are typically developed in immunized hosts (e.g., rabbits or mice) using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments corresponding to specific regions of ZNF434. Validated applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Specificity is confirmed via knockout/knockdown controls or competitive assays.
Research utilizing ZNF434 antibodies has linked the protein to potential roles in cancer progression, neurological disorders, and developmental regulation. However, its tissue-specific expression and regulatory mechanisms require further exploration. Commercial antibodies often provide data on reactivity across species (e.g., human, mouse, rat) and detailed epitope mapping. Users should verify experimental conditions (e.g., dilution ratios, fixation methods) to ensure reproducibility in their model systems.
×