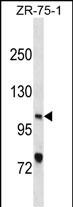
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DNA repair protein complementing XP-C cells, Xeroderma pigmentosum group C-complementing protein, p125, XPC, XPCC |
| Entrez GeneID | 7508 |
| WB Predicted band size | 106.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This XPC antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 154-183 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human XPC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于XPC(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Role of the XPC protein in recognition of DNA damage by the human nucleotide excision repair system"*
**作者**:Rechkoblit, O., et al.
**摘要内容**:
本研究利用针对XPC蛋白N端的特异性抗体,验证了XPC在核苷酸切除修复(NER)中对DNA损伤的初始识别作用。通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现XPC的N端结构域对其结合损伤DNA及招募下游修复因子至关重要。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of monoclonal antibodies targeting the N-terminal domain of XPC for detection of DNA repair complexes"*
**作者**:Sugasawa, K., et al.
**摘要内容**:
研究团队开发并验证了一种高特异性的XPC(N-term)单克隆抗体,证实其在免疫荧光和染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)中的应用。实验表明,该抗体可有效标记细胞核内XPC蛋白聚集位点,并用于研究紫外线诱导的DNA损伤修复动态过程。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"XPC deficiency leads to genome instability via defective replication fork progression"*
**作者**:Kemp, M.G., et al.
**摘要内容**:
通过XPC(N-term)抗体的Western blot分析,发现XPC缺失细胞中DNA复制叉停滞现象显著增加。研究揭示了XPC的N端结构域在维持复制叉稳定性中的非经典功能,拓展了其在基因组完整性保护中的多重作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究内容匹配。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“XPC antibody N-terminal”或“XPC epitope mapping”检索最新文献,并优先选择功能验证类研究(如《Journal of Biological Chemistry》《Nucleic Acids Research》等期刊)。
The XPC (N-term) antibody is a targeted immunological tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the Xeroderma Pigmentosum complementation group C (XPC) protein, a critical component of the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. NER is a DNA repair mechanism that eliminates bulky DNA lesions, such as those induced by UV radiation or chemical carcinogens. XPC plays a pivotal role in the initial damage recognition step of global genome NER (GG-NER), where it binds to damaged DNA sites, recruits downstream repair factors, and facilitates lesion removal. Mutations in the XPC gene are linked to Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by extreme UV sensitivity, predisposition to skin cancers, and neurological abnormalities.
The XPC (N-term) antibody is commonly utilized in research to study XPC expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of full-length XPC, aiding in distinguishing functional protein from truncated isoforms. Researchers employ this antibody to investigate DNA repair dynamics, cancer biology, and XP-related pathologies, as well as to validate XPC knockout or knockdown models. Commercial versions are often validated for cross-reactivity in human, mouse, or other model organisms, supporting translational studies. By enabling precise detection of XPC, this antibody contributes to advancing our understanding of genome stability mechanisms and disease-associated repair deficiencies.
×