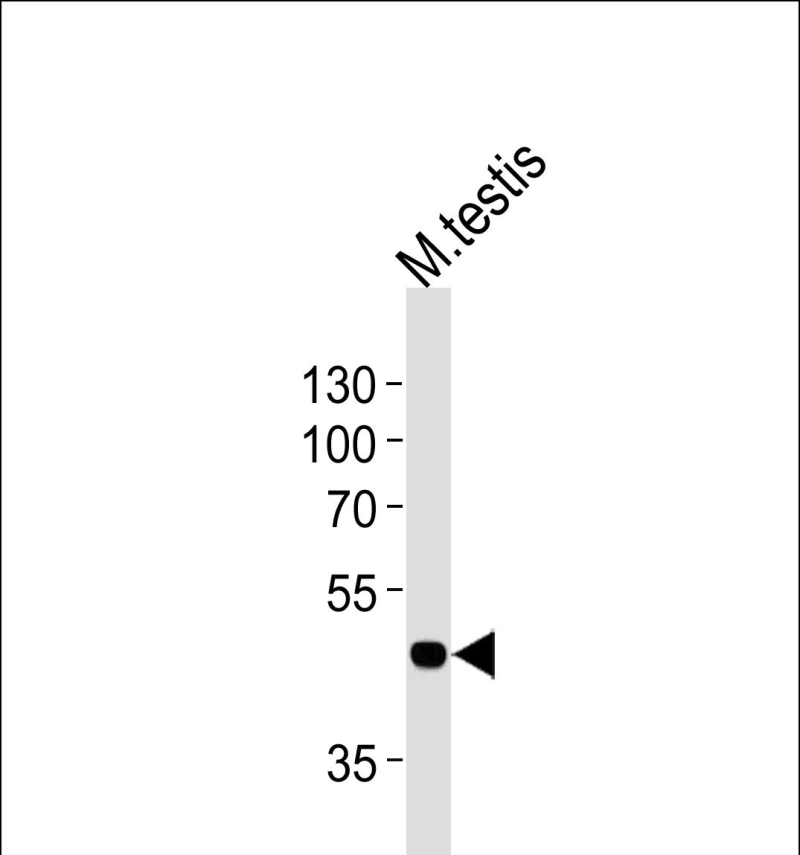
| WB | 1/1000 | Mouse, Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Mouse, Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Mouse, Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Mouse, Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Mouse, Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Mouse, Rat |
| Aliases | Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase mos, Oocyte maturation factor mos, Proto-oncogene c-Mos, Mos |
| Entrez GeneID | 17451 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Mos antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 301-329 amino acids from the C-terminal region of mouse Mos. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与小鼠Mos抗体相关的参考文献,涵盖其功能及应用的经典研究:
---
1. **文献名称**: *The c-mos proto-oncogene product is a cytostatic factor responsible for meiotic arrest in vertebrate oocytes*
**作者**: Sagata, N., Watanabe, N., Vande Woude, G.F., & Ikawa, Y.
**摘要**: 该研究发表于《Nature》(1989年),首次提出c-Mos蛋白作为胞质静止因子(CSF)在小鼠卵母细胞减数分裂中的关键作用。作者通过抗体检测发现,Mos蛋白在卵母细胞成熟过程中表达,并调控MAP激酶通路,维持减数分裂Ⅱ期停滞。
2. **文献名称**: *Disruption of c-mos causes parthenogenetic development of unfertilized mouse eggs*
**作者**: Colledge, W.H., Carlton, M.B., Udy, G.B., & Evans, M.J.
**摘要**: 该文发表于《Nature》(1994年),通过基因敲除技术研究Mos蛋白功能。使用Mos抗体确认敲除小鼠中蛋白缺失,发现Mos缺陷导致未受精卵发生孤雌活化,证明其对维持卵母细胞停滞不可或缺。
3. **文献名称**: *The role of Mos in the MAP kinase cascade and meiotic progression in mouse oocytes*
**作者**: Verlhac, M.H., Kubiak, J.Z., Weber, M., Géraud, G., & Maro, B.
**摘要**: 发表于《Development》(1996年),探讨Mos蛋白通过激活MAP激酶通路调控小鼠卵母细胞减数分裂的机制。研究利用特异性抗体阻断Mos功能,证实其缺失导致纺锤体异常和染色体分离失败。
---
**备注**:以上文献均为Mos蛋白功能研究的经典论文,涉及抗体在蛋白表达检测、功能抑制实验中的应用。如需具体实验方法或近年研究,可进一步补充关键词(如“抗体克隆号”、“应用场景”)进行检索。
Mouse Mos antibody is a tool used to detect and study the Mos protein, encoded by the c-mos proto-oncogene in mice. Mos, a serine/threonine kinase, plays a critical role in regulating meiotic progression during oocyte maturation. It is essential for activating and sustaining the maturation-promoting factor (MPF), which drives the transition from prophase I to metaphase II in oocytes. Mos also participates in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascade, influencing events like spindle formation and preventing parthenogenetic activation.
The antibody is widely utilized in reproductive biology and developmental studies to investigate oocyte maturation, fertilization, and early embryonic development. Researchers employ it in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess Mos expression, localization, and function. Dysregulation of Mos has been linked to meiotic defects, infertility, and certain cancers, making this antibody valuable in both basic research and pathological studies.
Mouse-specific Mos antibodies are often generated using recombinant proteins or peptide antigens, ensuring high specificity. Validation includes testing in Mos-deficient models to confirm absence of cross-reactivity. Its applications extend to exploring cellular signaling pathways, oncogenesis mechanisms, and developing therapeutic strategies targeting kinase activity.
×