
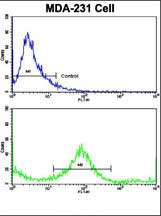
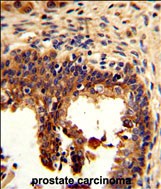
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 4, Cytokeratin-4, CK-4, Keratin-4, K4, Type-II keratin Kb4, KRT4, CYK4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3851 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This KRT4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 386-415 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KRT4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于KRT4抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Immunohistochemical localization of keratin 4 in oral white sponge nevus"*
**作者**: Arin, M.J., et al.
**摘要内容**: 本研究利用KRT4特异性抗体对口腔白色海绵状痣(WSN)患者的黏膜组织进行免疫组化分析。结果显示,与正常口腔黏膜相比,WSN病变区域的KRT4表达显著异常,表现为角蛋白丝网络的结构紊乱,支持KRT4突变在WSN发病机制中的作用,并验证了该抗体在诊断遗传性黏膜疾病中的有效性。
2. **文献名称**: *"Keratin 4 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a potential biomarker for tumor differentiation"*
**作者**: Takeda, H., et al.
**摘要内容**: 通过KRT4抗体检测食道鳞状细胞癌(ESCC)组织中的表达模式,研究发现KRT4在高分化肿瘤中高表达,而在低分化样本中表达缺失。结果表明,KRT4可作为ESCC分化程度的生物标志物,其抗体在病理分级中具有辅助诊断价值。
3. **文献名称**: *"Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody specific for human keratin 4"*
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要内容**: 本研究报道了一种新型抗人KRT4单克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验证实其高特异性和敏感性,且在不同上皮组织(如口腔、食道)中显示特异染色。该抗体为研究KRT4在正常生理及疾病中的功能提供了可靠工具。
---
以上文献涵盖了KRT4抗体在遗传病诊断、肿瘤分化评估及抗体开发中的应用,均通过实验验证了抗体的特异性与实用性。如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以标题及作者名进一步检索。
The KRT4 antibody is a tool used to detect keratin 4 (KRT4), a member of the type II keratin family, which forms intermediate filaments critical for maintaining structural integrity in epithelial cells. KRT4 is primarily expressed in non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelia, such as those lining the oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina. It pairs with keratin 13 (KRT13) to form heterodimers, contributing to cell resilience against mechanical stress.
KRT4 antibodies are widely employed in research and diagnostics to study epithelial differentiation, tissue-specific marker expression, and pathological conditions. For instance, reduced KRT4 expression is associated with squamous cell carcinomas and premalignant lesions, aiding in cancer progression studies. Additionally, mutations in the KRT4 gene are linked to white sponge nevus, a benign autosomal-dominant disorder characterized by oral and genital mucosal thickening.
In diagnostics, KRT4 antibodies help identify epithelial origin in metastatic tumors via immunohistochemistry. Their specificity also supports investigations into normal epithelial biology, wound healing, and genetic disorders affecting keratin networks. Overall, KRT4 antibodies serve as vital reagents for exploring epithelial cell biology and related diseases.
×