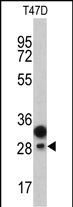
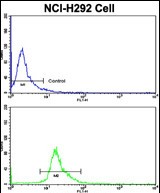
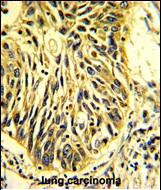
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Endothelial protein C receptor, Activated protein C receptor, APC receptor, Endothelial cell protein C receptor, CD201, PROCR, EPCR |
| Entrez GeneID | 10544 |
| WB Predicted band size | 26.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CD201 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 104-132 amino acids from the Central region of human CD201. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于CD201(EPCR)抗体的3篇参考文献,简要概述如下:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD201/EPCR promotes the stemness of acute myeloid leukemia cells by activating VEGF/HIF-α signaling*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过使用CD201抗体,揭示了CD201在急性髓系白血病(AML)干细胞中的高表达,并通过激活VEGF/HIF-α信号通路促进白血病细胞的自我更新和化疗耐药性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Endothelial protein C receptor (CD201) as a marker of tumor angiogenesis and potential therapeutic target*
**作者**: Kocher HM, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CD201抗体分析其在多种实体瘤(如胰腺癌和结直肠癌)血管内皮细胞中的表达,发现CD201高表达与肿瘤血管生成和不良预后相关,提示其可作为抗血管治疗的靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *CD201+ fibroblasts contribute to inflammation and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis*
**作者**: Asano Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化和流式细胞术结合CD201抗体,研究发现系统性硬化症患者皮肤中的CD201阳性成纤维细胞通过分泌促炎因子加剧组织纤维化,为疾病机制提供了新见解。
---
以上文献展示了CD201抗体在肿瘤生物学、血管生成及自身免疫性疾病研究中的应用。如需具体DOI或发表年份,可进一步补充检索。
CD201. also known as endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), is a cell surface glycoprotein encoded by the *PROCR* gene. It belongs to the CD molecule family and is primarily expressed on endothelial cells, particularly in large blood vessels, as well as on certain immune cells and stem cells. Structurally, CD201 contains a transmembrane domain and binds protein C or activated protein C (APC), playing a critical role in the anticoagulant pathway and cytoprotective signaling.
CD201 antibodies are valuable tools for studying vascular biology, inflammation, and coagulation disorders. In research, these antibodies help detect CD201 expression via flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or Western blotting, aiding in the identification of endothelial cell subsets or hematopoietic stem cells. CD201's involvement in APC-mediated anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant responses has linked it to pathologies like sepsis, thrombosis, and atherosclerosis. Recent studies also explore its role in cancer, where CD201 may influence tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.
Therapeutic targeting of CD201 is under investigation, particularly in conditions involving dysregulated coagulation or endothelial dysfunction. Commercially available CD201 antibodies vary in clonality (monoclonal/polyoclonal) and species reactivity, emphasizing the need for validation in specific experimental models. Its dual role in homeostasis and disease underscores CD201's significance as both a biomarker and a potential therapeutic target.
×