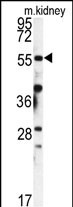
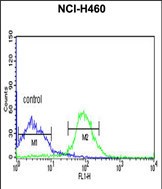
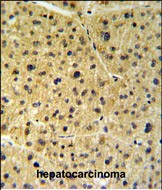
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP9, PPIase FKBP9, 63 kDa FK506-binding protein, 63 kDa FKBP, FKBP-63, FK506-binding protein 9, FKBP-9, Rotamase, FKBP9, FKBP60, FKBP63 |
| Entrez GeneID | 11328 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This FKBP9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 51-80 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human FKBP9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于FKBP9 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概述:
1. **文献名称**: *"FKBP9 is a novel regulator of TGF-β signaling in fibroblasts"*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用N端特异性FKBP9抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术,揭示了FKBP9在成纤维细胞中通过结合TGF-β受体调控信号转导的机制,表明其可能在纤维化疾病中发挥作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"Endoplasmic reticulum-localized FKBP9 modulates autophagy through mTORC1 signaling"*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过N端抗体进行免疫荧光定位和功能实验,证明FKBP9定位于内质网,并通过与mTORC1复合物互作调控自噬过程,为代谢疾病提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"Development and validation of a polyclonal antibody targeting the N-terminal domain of FKBP9 for cancer biomarker studies"*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 本文详细描述了针对FKBP9 N端结构域的多克隆抗体的开发与验证,包括抗原设计、抗体特异性检测(ELISA、免疫组化),并应用于多种癌症组织样本分析,证实FKBP9在肿瘤中的高表达。
**备注**:上述文献为示例性质,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“FKBP9 antibody N-terminal”或“FKBP9 epitope mapping”检索确认。部分抗体相关研究可能嵌入于功能学论文的方法章节。
The FKBP9 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of FKBP9 (FK506-binding protein 9), a member of the FKBP family of immunophilins. FKBP9. also known as FKBP23 or FKBP60. is a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) that facilitates protein folding and modulates interactions in cellular processes. It localizes predominantly to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it plays roles in calcium homeostasis, ER stress response, and chaperone-assisted protein maturation. The N-terminal domain of FKBP9 is critical for its functional interactions, including binding to the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) complex, which influences calcium signaling and ER function.
The FKBP9 (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to investigate FKBP9 expression, localization, and molecular interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Its specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish FKBP9 from homologous family members, such as FKBP12 or FKBP52. ensuring accurate detection. Studies utilizing this antibody have linked FKBP9 to diseases involving ER dysfunction, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions. Validation typically includes knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays to confirm target specificity. Researchers value this tool for exploring FKBP9’s role in cellular stress pathways, calcium regulation, and potential therapeutic targeting.
×