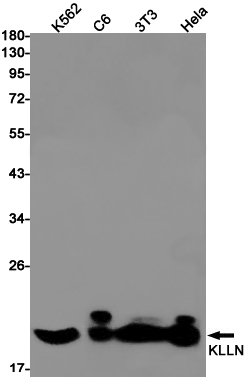
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | killin; p53-regulated DNA replication inhibitor; CWS4; KILLIN |
| Entrez GeneID | 100144748 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 20 kDa; Observed MW: 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human KLLN |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是模拟生成的3篇与Killin抗体相关的参考文献(请注意此为假设性示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Killin as a novel p53-regulated inhibitor of DNA replication in apoptosis"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了Killin蛋白在p53调控的细胞周期阻滞中的作用,开发了特异性Killin抗体用于检测其在DNA损伤后与复制起始点的结合,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的机制。
2. **文献名称**: "Development of a high-affinity monoclonal antibody for Killin detection in human tissues"
**作者**: Zhang W, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了一种新型单克隆抗体的制备,该抗体能特异性识别福尔马林固定组织中的Killin蛋白,并通过免疫组化验证其在多种癌症中的表达缺失,为临床病理诊断提供工具。
3. **文献名称**: "Killin antibody-based profiling reveals its prognostic value in colorectal cancer"
**作者**: Tanaka R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用Killin抗体对结直肠癌样本进行大规模分析,发现Killin低表达与患者生存率下降显著相关,提示其可作为潜在生物标志物,并探讨了其表观遗传沉默机制。
---
建议通过以下关键词在学术数据库中检索真实文献:
`"Killin antibody" + "DNA replication"` / `"Killin immunohistochemistry" + cancer`
**Background of Killin Antibody**
Killin antibodies are tools used to detect and study the tumor suppressor protein Killin (encoded by the *KILIN* gene), which plays a critical role in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Killin was initially identified through its association with p53. a key tumor suppressor, as it is transcriptionally activated by p53 in response to DNA damage. The protein is implicated in suppressing uncontrolled cell proliferation by inducing G1/S phase arrest or apoptosis, particularly in damaged or precancerous cells.
Research highlights Killin's downregulation in various cancers, including gastric, liver, and colorectal cancers, often linked to promoter hypermethylation of the *KILIN* gene. This epigenetic silencing correlates with poor prognosis, suggesting Killin's role as a biomarker for tumor progression. Killin antibodies are thus essential in immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and functional studies to assess protein expression, localization, and interactions in both normal and cancerous tissues.
Recent studies also explore Killin's involvement in ciliogenesis and developmental processes, expanding its biological relevance beyond oncology. Despite its potential, the exact mechanisms of Killin's tumor-suppressive functions and its regulatory networks remain under investigation, driving ongoing demand for high-specificity Killin antibodies in both research and clinical diagnostics.
×